Intravital microscopy as a tool to study drug delivery in preclinical studies
- PMID: 20933026
- PMCID: PMC3024442
- DOI: 10.1016/j.addr.2010.09.009
Intravital microscopy as a tool to study drug delivery in preclinical studies
Abstract
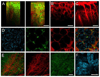
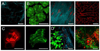
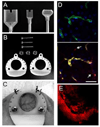
The technical developments in the field of non-linear microscopy have made intravital microscopy one of the most successful techniques for studying physiological and pathological processes in live animals. Intravital microscopy has been utilized to address many biological questions in basic research and is now a fundamental tool for preclinical studies, with an enormous potential for clinical applications. The ability to dynamically image cellular and subcellular structures combined with the possibility to perform longitudinal studies have empowered investigators to use this discipline to study the mechanisms of action of therapeutic agents and assess the efficacy on their targets in vivo. The goal of this review is to provide a general overview of the recent advances in intravital microscopy and to discuss some of its applications in preclinical studies.
Published by Elsevier B.V.
Figures
References
-
- Hoffman RM, Yang M. Whole-body imaging with fluorescent proteins. Nat Protoc. 2006;1:1429–1438. - PubMed
-
- Hyafil F, Cornily JC, Feig JE, Gordon R, Vucic E, Amirbekian V, Fisher EA, Fuster V, Feldman LJ, Fayad ZA. Noninvasive detection of macrophages using a nanoparticulate contrast agent for computed tomography. Nat Med. 2007;13:636–641. - PubMed
-
- Mitra A, Nan A, Line BR, Ghandehari H. Nanocarriers for nuclear imaging and radiotherapy of cancer. Curr Pharm Des. 2006;12:4729–4749. - PubMed
-
- Mulder WJ, Strijkers GJ, van Tilborg GA, Griffioen AW, Nicolay K. Lipid-based nanoparticles for contrast-enhanced MRI and molecular imaging. NMR Biomed. 2006;19:142–164. - PubMed
-
- Yang M, Jiang P, Hoffman RM. Whole-body subcellular multicolor imaging of tumor-host interaction and drug response in real time. Cancer Res. 2007;67:5195–5200. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

