Cancer secretomics reveal pathophysiological pathways in cancer molecular oncology
- PMID: 20934395
- PMCID: PMC5527923
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molonc.2010.09.001
Cancer secretomics reveal pathophysiological pathways in cancer molecular oncology
Abstract
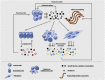
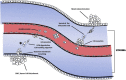
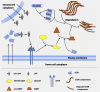
Emerging proteomic tools and mass spectrometry play pivotal roles in protein identification, quantification and characterization, even in complex biological samples. The cancer secretome, namely the whole collection of proteins secreted by cancer cells through various secretory pathways, has only recently been shown to have significant potential for diverse applications in oncoproteomics. For example, secreted proteins might represent putative tumor biomarkers or therapeutic targets for various types of cancer. Consequently, many proteomic strategies for secretome analysis have been extensively deployed over the last few years. These efforts generated a large amount of information awaiting deeper mining, better understanding and careful interpretation. Distinct sub-fields, such as degradomics, exosome proteomics and tumor-host cell interactions have been developed, in an attempt to provide certain answers to partially elucidated mechanisms of cancer pathobiology. In this review, advances, concerns and challenges in the field of secretome analysis as well as possible clinical applications are discussed.
Copyright © 2010 Federation of European Biochemical Societies. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Aebersold, R. , Mann, M. , 2003. Mass spectrometry-based proteomics. Nature. 422, (6928) 198–207. - PubMed
-
- Bendtsen, J.D. , Jensen, L.J. , 2004. Feature-based prediction of non-classical and leaderless protein secretion. Protein Eng. Des Sel. 17, (4) 349–356. - PubMed
-
- Bendtsen, J.D. , Nielsen, H. , 2004. Improved prediction of signal peptides: signalP 3.0. J. Mol. Biol. 340, (4) 783–795. - PubMed
-
- Bialkowska, K. , Zaffran, Y. , 2003. 14-3-3 zeta mediates integrin-induced activation of Cdc42 and Rac. Platelet glycoprotein Ib-IX regulates integrin-induced signaling by sequestering 14-3-3 zeta. J. Biol. Chem. 278, (35) 33342–33350. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

