The hepatitis B virus HBx protein modulates cell cycle regulatory proteins in cultured primary human hepatocytes
- PMID: 20934470
- PMCID: PMC3010534
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virusres.2010.09.023
The hepatitis B virus HBx protein modulates cell cycle regulatory proteins in cultured primary human hepatocytes
Abstract
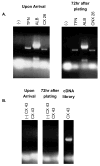
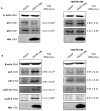
There are over 350 million people chronically infected with the Hepatitis B virus (HBV); chronic HBV infections are associated with the development of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). While the precise mechanism of HBV-associated HCC remains undefined, it is believed to involve a combination of the host immune response to infection and activities of HBV proteins including the nonstructural X protein (HBx). HBx is a multifunctional protein that can modulate various cellular processes including cell proliferation. The exact effect of HBx on cell proliferation has varied depending on the cell line and exact conditions used in the study. Our previously published reports have demonstrated that HBx modulates the levels of cell cycle regulatory proteins in primary rat hepatocytes; however, the effect of HBx on cell cycle regulatory proteins in primary human hepatocytes, the natural host for HBV infection, has not been studied. Here we have examined the effect of HBx on cell cycle regulatory proteins in cultured, primary human hepatocytes. We demonstrate that HBx decreases the levels of cell cycle proteins that prevent progression into G1 phase and increases the levels of cell cycle proteins active in G1 phase. We have also shown that HBx modulation of cell cycle regulatory proteins requires cytosolic calcium, similar to the results we previously obtained in primary rat hepatocytes. Cumulatively, our results are the first demonstration that HBx modulates the levels of cell cycle regulatory proteins in a calcium-dependent manner in primary human hepatocytes.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Modulation of apoptotic signaling by the hepatitis B virus X protein.Viruses. 2012 Nov 8;4(11):2945-72. doi: 10.3390/v4112945. Viruses. 2012. PMID: 23202511 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The hepatitis B virus X protein modulates hepatocyte proliferation pathways to stimulate viral replication.J Virol. 2010 Mar;84(6):2675-86. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02196-09. Epub 2010 Jan 6. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20053744 Free PMC article.
-
Replication of the hepatitis B virus requires a calcium-dependent HBx-induced G1 phase arrest of hepatocytes.Virology. 2010 Nov 10;407(1):14-25. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2010.07.042. Epub 2010 Aug 16. Virology. 2010. PMID: 20719353 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatitis B virus modulates store-operated calcium entry to enhance viral replication in primary hepatocytes.PLoS One. 2017 Feb 2;12(2):e0168328. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0168328. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28151934 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatitis B virus, HBx mutants and their role in hepatocellular carcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Aug 14;20(30):10238-48. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i30.10238. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25132741 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A southern blot assay for detection of hepatitis B virus covalently closed circular DNA from cell cultures.Methods Mol Biol. 2013;1030:151-61. doi: 10.1007/978-1-62703-484-5_13. Methods Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23821267 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of apoptotic signaling by the hepatitis B virus X protein.Viruses. 2012 Nov 8;4(11):2945-72. doi: 10.3390/v4112945. Viruses. 2012. PMID: 23202511 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptome-Wide Analysis of Hepatitis B Virus-Mediated Changes to Normal Hepatocyte Gene Expression.PLoS Pathog. 2016 Feb 18;12(2):e1005438. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005438. eCollection 2016 Feb. PLoS Pathog. 2016. PMID: 26891448 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatitis B Virus X and Regulation of Viral Gene Expression.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2016 Jan 8;6(3):a021402. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a021402. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2016. PMID: 26747833 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell cycle regulation during viral infection.Methods Mol Biol. 2014;1170:165-227. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-0888-2_10. Methods Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 24906315 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ahn JY, Chung EY, Kwun HJ, Jang KL. Transcriptional repression of p21(waf1) promoter by hepatitis B virus X protein via a p53-independent pathway. Gene. 2001;275(1):163–8. - PubMed
-
- Block GD, Locker J, Bowen WC, Petersen BE, Katyal S, Strom SC, Riley T, Howard TA, Michalopoulos GK. Population expansion, clonal growth, and specific differentiation patterns in primary cultures of hepatocytes induced by HGF/SF, EGF and TGF alpha in a chemically defined (HGM) medium. J Cell Biol. 1996;132(6):1133–49. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chin R, Earnest-Silveira L, Koeberlein B, Franz S, Zentgraf H, Dong X, Gowans E, Bock CT, Torresi J. Modulation of MAPK pathways and cell cycle by replicating hepatitis B virus: factors contributing to hepatocarcinogenesis. J Hepatol. 2007;47(3):325–37. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

