Notch dimerization is required for leukemogenesis and T-cell development
- PMID: 20935071
- PMCID: PMC2964750
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1975210
Notch dimerization is required for leukemogenesis and T-cell development
Abstract
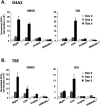
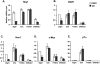
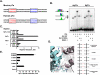
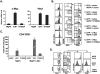
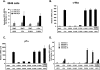
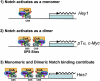
Notch signaling regulates myriad cellular functions by activating transcription, yet how Notch selectively activates different transcriptional targets is poorly understood. The core Notch transcriptional activation complex can bind DNA as a monomer, but it can also dimerize on DNA-binding sites that are properly oriented and spaced. However, the significance of Notch dimerization is unknown. Here, we show that dimeric Notch transcriptional complexes are required for T-cell maturation and leukemic transformation but are dispensable for T-cell fate specification from a multipotential precursor. The varying requirements for Notch dimerization result from the differential sensitivity of specific Notch target genes. In particular, c-Myc and pre-T-cell antigen receptor α (Ptcra) are dimerization-dependent targets, whereas Hey1 and CD25 are not. These findings identify functionally important differences in the responsiveness among Notch target genes attributable to the formation of higher-order complexes. Consequently, it may be possible to develop a new class of Notch inhibitors that selectively block outcomes that depend on Notch dimerization (e.g., leukemogenesis).
Figures

References
-
- Aifantis I, Mandal M, Sawai K, Ferrando A, Vilimas T 2006. Regulation of T-cell progenitor survival and cell-cycle entry by the pre-T-cell receptor. Immunol Rev 209: 159–169 - PubMed
-
- Artavanis-Tsakonas S, Rand MD, Lake RJ 1999. Notch signaling: Cell fate control and signal integration in development. Science 284: 770–776 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AI047833/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK007780/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01CA119070/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG02666/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA092433/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA009140/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32-CA009140/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 CA120544-01/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- RC1 HL099758/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RC1HL099758/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 CA120544/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA119070/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01AI047833/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32-DK07780/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
