Population genetics meets cancer genomics
- PMID: 20935251
- PMCID: PMC2972988
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1013177107
Population genetics meets cancer genomics
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: Martin Nowak, the last author of Bozic et al. (6), was the author's master's degree thesis advisor (1996–1998).
Figures
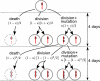
Comment on
-
Accumulation of driver and passenger mutations during tumor progression.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Oct 26;107(43):18545-50. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1010978107. Epub 2010 Sep 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20876136 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

