Prolonged drug selection of breast cancer cells and enrichment of cancer stem cell characteristics
- PMID: 20935265
- PMCID: PMC2970576
- DOI: 10.1093/jnci/djq361
Prolonged drug selection of breast cancer cells and enrichment of cancer stem cell characteristics
Abstract
Background: Cancer stem cells are presumed to have virtually unlimited proliferative and self-renewal abilities and to be highly resistant to chemotherapy, a feature that is associated with overexpression of ATP-binding cassette transporters. We investigated whether prolonged continuous selection of cells for drug resistance enriches cultures for cancer stem-like cells.
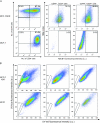
Methods: Cancer stem cells were defined as CD44+/CD24⁻ cells that could self-renew (ie, generate cells with the tumorigenic CD44+/CD24⁻ phenotype), differentiate, invade, and form tumors in vivo. We used doxorubicin-selected MCF-7/ADR cells, weakly tumorigenic parental MCF-7 cells, and MCF-7/MDR, an MCF-7 subline with forced expression of ABCB1 protein. Cells were examined for cell surface markers and side-population fractions by microarray and flow cytometry, with in vitro invasion assays, and for ability to form mammospheres. Xenograft tumors were generated in mice to examine tumorigenicity (n = 52). The mRNA expression of multidrug resistance genes was examined in putative cancer stem cells and pathway analysis of statistically significantly differentially expressed genes was performed. All statistical tests were two-sided.
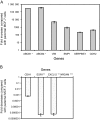
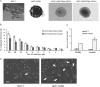
Results: Pathway analysis showed that MCF-7/ADR cells express mRNAs from ABCB1 and other genes also found in breast cancer stem cells (eg, CD44, TGFB1, and SNAI1). MCF-7/ADR cells were highly invasive, formed mammospheres, and were tumorigenic in mice. In contrast to parental MCF-7 cells, more than 30% of MCF-7/ADR cells had a CD44+/CD24⁻ phenotype, could self-renew, and differentiate (ie, produce CD44+/CD24⁻ and CD44+/CD24+ cells) and overexpressed various multidrug resistance-linked genes (including ABCB1, CCNE1, and MMP9). MCF-7/ADR cells were statistically significantly more invasive in Matrigel than parental MCF-7 cells (MCF-7 cells = 0.82 cell per field and MCF-7/ADR = 7.51 cells per field, difference = 6.69 cells per field, 95% confidence interval = 4.82 to 8.55 cells per field, P < .001). No enrichment in the CD44+/CD24⁻ or CD133+ population was detected in MCF-7/MDR.
Conclusion: The cell population with cancer stem cell characteristics increased after prolonged continuous selection for doxorubicin resistance.
Figures

References
-
- Gottesman M, Fojo T, Bates S. Multidrug resistance in cancer: role of ATP-dependent transporters. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2(1):48–58. - PubMed
-
- Calcagno AM, Kim IW, Wu CP, Shukla S, Ambudkar SV. ABC drug transporters as molecular targets for the prevention of multidrug resistance and drug-drug interactions. Curr Drug Deliv. 2007;4(4):324–333. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

