Aubergine is a component of a nanos mRNA localization complex
- PMID: 20937269
- PMCID: PMC2993811
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2010.10.002
Aubergine is a component of a nanos mRNA localization complex
Abstract
Localization of nanos (nos) mRNA to the posterior pole of the Drosophila oocyte is essential for abdominal segmentation and germline development during embryogenesis. Posterior localization is mediated by a complex cis-acting localization signal in the nos 3' untranslated region that comprises multiple partially redundant elements. Genetic analysis suggests that this signal is recognized by RNA-binding proteins and associated factors that package nos mRNA into a localization competent ribonucleoprotein complex. However, functional redundancy among localization elements has made the identification of individual localization factors difficult. Indeed, only a single direct-acting nos localization factor, Rumpelstiltskin (Rump), has been identified thus far. Through a sensitized genetic screen, we have now identified the Argonaute family member Aubergine (Aub) as a nos localization factor. Aub interacts with nos mRNA in vivo and co-purifies with Rump in an RNA-dependent manner. Our results support a role for Aub, independent of its function in RNA silencing, as a component of a nos mRNA localization complex.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

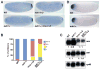
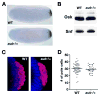
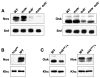
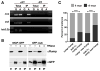
Similar articles
-
Maternal mRNA deadenylation and decay by the piRNA pathway in the early Drosophila embryo.Nature. 2010 Oct 28;467(7319):1128-32. doi: 10.1038/nature09465. Epub 2010 Oct 17. Nature. 2010. PMID: 20953170 Free PMC article.
-
The Drosophila hnRNP M homolog Rumpelstiltskin regulates nanos mRNA localization.Development. 2008 Mar;135(5):973-82. doi: 10.1242/dev.015438. Epub 2008 Jan 30. Development. 2008. PMID: 18234721
-
Recognition and long-range interactions of a minimal nanos RNA localization signal element.Development. 2001 Feb;128(3):427-35. doi: 10.1242/dev.128.3.427. Development. 2001. PMID: 11152641
-
Dynein-dependent transport of nanos RNA in Drosophila sensory neurons requires Rumpelstiltskin and the germ plasm organizer Oskar.J Neurosci. 2013 Sep 11;33(37):14791-800. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5864-12.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 24027279 Free PMC article.
-
The molecular chaperone Hsp90 is required for mRNA localization in Drosophila melanogaster embryos.Genetics. 2007 Aug;176(4):2213-22. doi: 10.1534/genetics.107.071472. Epub 2007 Jun 11. Genetics. 2007. PMID: 17565952 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The 3'UTR of nanos2 directs enrichment in the germ cell lineage of the sea urchin.Dev Biol. 2013 May 1;377(1):275-83. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2013.01.019. Epub 2013 Jan 25. Dev Biol. 2013. PMID: 23357540 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and functional organization of germ plasm condensates.Biochem J. 2022 Dec 19;479(24):2477-2495. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20210815. Biochem J. 2022. PMID: 36534469 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein components of ribonucleoprotein granules from Drosophila germ cells oligomerize and show distinct spatial organization during germline development.Sci Rep. 2019 Dec 16;9(1):19190. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-55747-x. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31844131 Free PMC article.
-
Xenopus Piwi proteins interact with a broad proportion of the oocyte transcriptome.RNA. 2017 Apr;23(4):504-520. doi: 10.1261/rna.058859.116. Epub 2016 Dec 28. RNA. 2017. PMID: 28031481 Free PMC article.
-
Rbm24a dictates mRNA recruitment for germ granule assembly in zebrafish.EMBO J. 2025 Jun;44(11):3121-3149. doi: 10.1038/s44318-025-00442-z. Epub 2025 Apr 25. EMBO J. 2025. PMID: 40281355 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdu U, Brodsky M, Schupbach T. Activation of a meiotic checkpoint during Drosophila oogenesis regulates the translation of Gurken through Chk2/Mnk. Curr Biol. 2002;12:1645–1651. - PubMed
-
- Bergsten SE, Gavis ER. Role for mRNA localization in translational activation but not spatial restriction of nanos RNA. Development. 1999;126:659–669. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

