Gating of a G protein-sensitive mammalian Kir3.1 prokaryotic Kir channel chimera in planar lipid bilayers
- PMID: 20937804
- PMCID: PMC3000960
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.151373
Gating of a G protein-sensitive mammalian Kir3.1 prokaryotic Kir channel chimera in planar lipid bilayers
Abstract
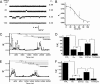
Kir3 channels control heart rate and neuronal excitability through GTP-binding (G) protein and phosphoinositide signaling pathways. These channels were the first characterized effectors of the βγ subunits of G proteins. Because we currently lack structures of complexes between G proteins and Kir3 channels, their interactions leading to modulation of channel function are not well understood. The recent crystal structure of a chimera between the cytosolic domain of a mammalian Kir3.1 and the transmembrane region of a prokaryotic KirBac1.3 (Kir3.1 chimera) has provided invaluable structural insight. However, it was not known whether this chimera could form functional K(+) channels. Here, we achieved the functional reconstitution of purified Kir3.1 chimera in planar lipid bilayers. The chimera behaved like a bona fide Kir channel displaying an absolute requirement for PIP(2) and Mg(2+)-dependent inward rectification. The channel could also be blocked by external tertiapin Q. The three-dimensional reconstruction of the chimera by single particle electron microscopy revealed a structure consistent with the crystal structure. Channel activity could be stimulated by ethanol and activated G proteins. Remarkably, the presence of both activated Gα and Gβγ subunits was required for gating of the channel. These results confirm the Kir3.1 chimera as a valid structural and functional model of Kir3 channels.
Figures
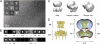





References
-
- Huang C. L., Feng S., Hilgemann D. W. (1998) Nature 391, 803–806 - PubMed
-
- Logothetis D. E., Kurachi Y., Galper J., Neer E. J., Clapham D. E. (1987) Nature 325, 321–326 - PubMed
-
- Reuveny E., Slesinger P. A., Inglese J., Morales J. M., Iñiguez-Lluhi J. A., Lefkowitz R. J., Bourne H. R., Jan Y. N., Jan L. Y. (1994) Nature 370, 143–146 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

