IL-33 is a crucial amplifier of innate rather than acquired immunity
- PMID: 20937871
- PMCID: PMC2972966
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1003059107
IL-33 is a crucial amplifier of innate rather than acquired immunity
Abstract
IL-33, a member of the IL-1-related cytokines, is considered to be a proallergic cytokine that is especially involved in Th2-type immune responses. Moreover, like IL-1α, IL-33 has been suggested to act as an "alarmin" that amplifies immune responses during tissue injury. In contrast to IL-1, however, the precise roles of IL-33 in those settings are poorly understood. Using IL-1- and IL-33-deficient mice, we found that IL-1, but not IL-33, played a substantial role in induction of T cell-mediated type IV hypersensitivity such as contact and delayed-type hypersensitivity and autoimmune diseases such as experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Most notably, however, IL-33 was important for innate-type mucosal immunity in the lungs and gut. That is, IL-33 was essential for manifestation of T cell-independent protease allergen-induced airway inflammation as well as OVA-induced allergic topical airway inflammation, without affecting acquisition of antigen-specific memory T cells. IL-33 was significantly involved in the development of dextran-induced colitis accompanied by T cell-independent epithelial cell damage, but not in streptozocin-induced diabetes or Con A-induced hepatitis characterized by T cell-mediated apoptotic tissue destruction. In addition, IL-33-deficient mice showed a substantially diminished LPS-induced systemic inflammatory response. These observations indicate that IL-33 is a crucial amplifier of mucosal and systemic innate, rather than acquired, immune responses.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
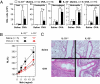

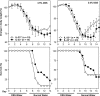

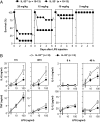
References
-
- Schmitz J, et al. IL-33, an interleukin-1-like cytokine that signals via the IL-1 receptor-related protein ST2 and induces T helper type 2-associated cytokines. Immunity. 2005;23:479–490. - PubMed
-
- Smith DE. IL-33: A tissue derived cytokine pathway involved in allergic inflammation and asthma. Clin Exp Allergy. 2010;40:200–208. - PubMed
-
- Liew FY, Pitman NI, McInnes IB. Disease-associated functions of IL-33: The new kid in the IL-1 family. Nat Rev Immunol. 2010;10:103–110. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

