Intracellular expression of IRF9 Stat fusion protein overcomes the defective Jak-Stat signaling and inhibits HCV RNA replication
- PMID: 20939906
- PMCID: PMC2964675
- DOI: 10.1186/1743-422X-7-265
Intracellular expression of IRF9 Stat fusion protein overcomes the defective Jak-Stat signaling and inhibits HCV RNA replication
Abstract
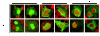
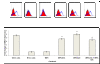
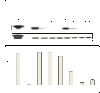
Interferon alpha (IFN-α) binds to a cell surface receptor that activates the Jak-Stat signaling pathway. A critical component of this pathway is the translocation of interferon stimulated gene factor 3 (a complex of three proteins Stat1, Stat2 and IRF9) to the nucleus to activate antiviral genes. A stable sub-genomic replicon cell line resistant to IFN-α was developed in which the nuclear translocation of Stat1 and Stat2 proteins was prevented due to the lack of phosphorylation; whereas the nuclear translocation of IRF9 protein was not affected. In this study, we sought to overcome defective Jak-Stat signaling and to induce an antiviral state in the IFN-α resistant replicon cell line by developing a chimera IRF9 protein fused with the trans activating domain (TAD) of either a Stat1 (IRF9-S1C) or Stat2 (IRF9-S2C) protein. We show here that intracellular expression of fusion proteins using the plasmid constructs of either IRF9-S1C or IRF9-S2C, in the IFN-α resistant cells, resulted in an increase in Interferon Stimulated Response Element (ISRE) luciferase promoter activity and significantly induced HLA-1 surface expression. Moreover, we show that transient transfection of IRF9-S1C or IRF9-S2C plasmid constructs into IFN-α resistant replicon cells containing sub-genomic HCV1b and HCV2a viruses resulted in an inhibition of viral replication and viral protein expression independent of IFN-α treatment. The results of this study indicate that the recombinant fusion proteins of IRF9-S1C, IRF9-S2C alone, or in combination, have potent antiviral properties against the HCV in an IFN-α resistant cell line with a defective Jak-Stat signaling.
Figures


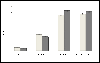



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

