Role of ionotropic GABA, glutamate and glycine receptors in the tonic and reflex control of cardiac vagal outflow in the rat
- PMID: 20939929
- PMCID: PMC2964734
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2202-11-128
Role of ionotropic GABA, glutamate and glycine receptors in the tonic and reflex control of cardiac vagal outflow in the rat
Abstract
Background: Cardiac vagal preganglionic neurons (CVPN) are responsible for the tonic, reflex and respiratory modulation of heart rate (HR). Although CVPN receive GABAergic and glutamatergic inputs, likely involved in respiratory and reflex modulation of HR respectively, little else is known regarding the functions controlled by ionotropic inputs. Activation of g-protein coupled receptors (GPCR) alters these inputs, but the functional consequence is largely unknown. The present study aimed to delineate how ionotropic GABAergic, glycinergic and glutamatergic inputs contribute to the tonic and reflex control of HR and in particular determine which receptor subtypes were involved. Furthermore, we wished to establish how activation of the 5-HT1A GPCR affects tonic and reflex control of HR and what ionotropic interactions this might involve.
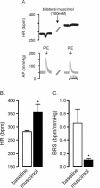
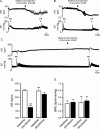
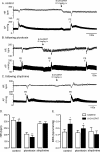
Results: Microinjection of the GABAA antagonist picrotoxin into CVPN decreased HR but did not affect baroreflex bradycardia. The glycine antagonist strychnine did not alter HR or baroreflex bradycardia. Combined microinjection of the NMDA antagonist, MK801, and AMPA antagonist, CNQX, into CVPN evoked a small bradycardia and abolished baroreflex bradycardia. MK801 attenuated whereas CNQX abolished baroreceptor bradycardia. Control intravenous injections of the 5-HT1A agonist 8-OH-DPAT evoked a small bradycardia and potentiated baroreflex bradycardia. These effects were still observed following microinjection of picrotoxin but not strychnine into CVPN.
Conclusions: We conclude that activation of GABAA receptors set the level of HR whereas AMPA to a greater extent than NMDA receptors elicit baroreflex changes in HR. Furthermore, activation of 5-HT1A receptors evokes bradycardia and enhances baroreflex changes in HR due to interactions with glycinergic neurons involving strychnine receptors. This study provides reference for future studies investigating how diseases alter neurochemical inputs to CVPN.
Figures

Similar articles
-
5-HT1A/7 receptor agonist excites cardiac vagal neurons via inhibition of both GABAergic and glycinergic inputs.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2008 May;29(5):529-38. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-7254.2008.00745.x. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2008. PMID: 18430360
-
Glycinergic neurotransmission in the rostral ventrolateral medulla controls the time course of baroreflex-mediated sympathoinhibition.J Physiol. 2019 Jan;597(1):283-301. doi: 10.1113/JP276467. Epub 2018 Nov 22. J Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30312491 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of the purinergic system in central cardiovascular modulation at the level of the nucleus ambiguus of anaesthetized rats.Exp Physiol. 2011 Mar;96(3):262-74. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.2010.054882. Epub 2010 Dec 10. Exp Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21148626
-
Serotonin2 receptors in the nucleus tractus solitarius: characterization and role in the baroreceptor reflex arc.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2003 Oct;23(4-5):709-26. doi: 10.1023/a:1025096718559. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2003. PMID: 14514026 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Medullary and supramedullary mechanisms regulating sympathetic vasomotor tone.Acta Physiol Scand. 2003 Mar;177(3):209-18. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-201X.2003.01070.x. Acta Physiol Scand. 2003. PMID: 12608991 Review.
Cited by
-
The effects of the modulation of NMDA receptors by homocysteine thiolactone and dizocilpine on cardiodynamics and oxidative stress in isolated rat heart.Mol Cell Biochem. 2015 Mar;401(1-2):97-105. doi: 10.1007/s11010-014-2296-8. Epub 2014 Dec 3. Mol Cell Biochem. 2015. PMID: 25467376
-
Genetic locus on mouse chromosome 7 controls elevated heart rate.Physiol Genomics. 2012 Jul 3;44(13):689-98. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00041.2012. Epub 2012 May 15. Physiol Genomics. 2012. PMID: 22589454 Free PMC article.
-
Gastrodin improved baroreflex sensitivity and increased gamma-amino butyric acid content in brains without decreasing blood pressure in spontaneously hypertensive rats.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2012 Oct;18(10):873-5. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-5949.2012.00381.x. Epub 2012 Aug 20. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2012. PMID: 22900998 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Multivariate analysis of subjective responses to d-amphetamine in healthy volunteers finds novel genetic pathway associations.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2015 Aug;232(15):2781-94. doi: 10.1007/s00213-015-3914-1. Epub 2015 Apr 7. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2015. PMID: 25843748 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiovascular afferents cause the release of 5-HT in the nucleus tractus solitarii; this release is regulated by the low- (PMAT) not the high-affinity transporter (SERT).J Physiol. 2015 Apr 1;593(7):1715-29. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2014.285312. Epub 2015 Feb 19. J Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25694117 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Thompson ME, Felsten G, Yavorsky J, Natelson BH. Differential effect of stimulation of nucleus ambiguus on atrial and ventricular rates. American Journal of Physiology. 1987;253(1):R150–R157. - PubMed
-
- Geis G, Wurster R. Cardiac responses during stimulation of the dorsal motor nucleus and nucleus ambiguus in the cat. Circ Res. 1980;46(5):606–611. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

