N-terminal and C-terminal heparin-binding domain polypeptides derived from fibronectin reduce adhesion and invasion of liver cancer cells
- PMID: 20939933
- PMCID: PMC2965728
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-10-552
N-terminal and C-terminal heparin-binding domain polypeptides derived from fibronectin reduce adhesion and invasion of liver cancer cells
Abstract
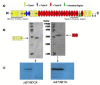
Background: Fibronectin (FN) is known to be a large multifunction glycoprotein with binding sites for many substances, including N-terminal and C-terminal heparin-binding domains. We investigated the effects of highly purified rhFNHN29 and rhFNHC36 polypeptides originally cloned from the two heparin-binding domains on the adhesion and invasion of highly metastatic human hepatocellular carcinoma cells (MHCC97H) and analyzed the underlying mechanism involved.
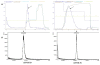
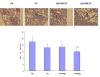
Methods: The MHCC97H cells that adhered to FN in the presence of various concentrations of rhFNHN29 and rhFNHC36 polypeptides were stained with crystal violet and measured, and the effects of rhFNHN29 and rhFNHC36 on the invasion of the MHCC97H cells were then detected using the Matrigel invasion assay as well as a lung-metastasis mouse model. The expression level of integrins and focal adhesion kinase (FAK) phosphotyrosyl protein was examined by Western blot, and the activity of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and activator protein 1 (AP-1) was analyzed by gelatin zymography and the electrophoretic mobility band-shift assay (EMSA), respectively.
Results: Both of the polypeptides rhFNHN29 and rhFNHC36 inhibited adhesion and invasion of MHCC97H cells; however, rhFNHC36 exhibited inhibition at a lower dose than rhFNHN29. These inhibitory effects were mediated by integrin αvβ3 and reversed by a protein tyrosine phosphatase inhibitor. Polypeptides rhFNHN29 and rhFNHC36 abrogated the tyrosine phosphorylation of focal adhesion kinase (p-FAK) and activation of activator protein 1 (AP-1), resulting in the decrease of integrin αv, β3 and β1 expression as well as the reduction of MMP-9 activity.
Conclusions: Polypeptides rhFNHN29 and rhFNHC36 could potentially be applicable to human liver cancer as anti-adhesive and anti-invasive agents.
Figures
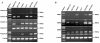



Similar articles
-
Role of Ets-1 in fibronectin-derived heparin-binding domain polypeptides alleviating melanoma cell invasiveness and chemoresistance.Exp Dermatol. 2014 Jul;23(7):512-3. doi: 10.1111/exd.12444. Exp Dermatol. 2014. PMID: 24816403
-
Autocrine motility factor enhances hepatoma cell invasion across the basement membrane through activation of beta1 integrins.Hepatology. 2001 Jul;34(1):62-71. doi: 10.1053/jhep.2001.25546. Hepatology. 2001. PMID: 11431735
-
C-terminal heparin-binding domain of fibronectin regulates integrin-mediated cell spreading but not the activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase.Biochem J. 2001 Nov 15;360(Pt 1):239-45. doi: 10.1042/0264-6021:3600239. Biochem J. 2001. PMID: 11696013 Free PMC article.
-
Down-regulation of N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase V by tumorigenesis- or metastasis-suppressor gene and its relation to metastatic potential of human hepatocarcinoma cells.J Cell Biochem. 2000 Sep 7;79(3):370-85. doi: 10.1002/1097-4644(20001201)79:3<370::aid-jcb30>3.0.co;2-z. J Cell Biochem. 2000. PMID: 10972975
-
Functional effect of contortrostatin, a snake venom disintegrin, on human glioma cell invasion in vitro.Cell Commun Adhes. 2003 Jan-Feb;10(1):1-16. doi: 10.1080/15419060302062. Cell Commun Adhes. 2003. PMID: 12881036
Cited by
-
Urokinase-derived peptide UP-7 suppresses tumor angiogenesis and metastasis through inhibition of FAK activation.Oncotarget. 2018 Jan 10;9(11):9951-9962. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.24131. eCollection 2018 Feb 9. Oncotarget. 2018. PMID: 29515782 Free PMC article.
-
Suppressive effect of syndecan ectodomains and N-desulfated heparins on osteoclastogenesis via direct binding to macrophage-colony stimulating factor.Cell Death Dis. 2018 Nov 2;9(11):1119. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-1167-8. Cell Death Dis. 2018. PMID: 30389911 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulation of fibronectin 1 attenuates ATRA-induced inhibition of cell migration and invasion in neuroblastoma cells.Mol Cell Biochem. 2021 Oct;476(10):3601-3612. doi: 10.1007/s11010-021-04113-5. Epub 2021 May 22. Mol Cell Biochem. 2021. PMID: 34024029
-
Extracellular matrix bioengineering and systems biology approaches in liver disease.Syst Synth Biol. 2011 Jun;5(1-2):11-20. doi: 10.1007/s11693-011-9085-4. Epub 2011 Jun 17. Syst Synth Biol. 2011. PMID: 22654992 Free PMC article.
-
Fibronectin Mechanobiology Regulates Tumorigenesis.Cell Mol Bioeng. 2016;9:1-11. doi: 10.1007/s12195-015-0417-4. Epub 2015 Aug 15. Cell Mol Bioeng. 2016. PMID: 26900407 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Song G, Ohashi T, Sakamoto N, Sato M. Adhesive force of human hepatoma HepG2 cells to endothelial cells and expression of E-selectin. Mol Cell Biomech. 2006;3(2):61–68. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

