BMP antagonists enhance myogenic differentiation and ameliorate the dystrophic phenotype in a DMD mouse model
- PMID: 20940052
- PMCID: PMC3674857
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nbd.2010.10.003
BMP antagonists enhance myogenic differentiation and ameliorate the dystrophic phenotype in a DMD mouse model
Abstract
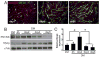
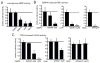
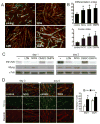
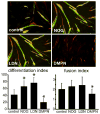
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) is an X-linked lethal muscle wasting disease characterized by muscle fiber degeneration and necrosis. The progressive pathology of DMD can be explained by an insufficient regenerative response resulting in fibrosis and adipose tissue formation. BMPs are known to inhibit myogenic differentiation and in a previous study we found an increased expression of a BMP family member BMP4 in DMD myoblasts. The aim of the current study was therefore to investigate whether inhibition of BMP signaling could be beneficial for myoblast differentiation and muscle regeneration processes in a DMD context. All tested BMP inhibitors, Noggin, dorsomorphin and LDN-193189, were able to accelerate and enhance myogenic differentiation. However, dorsomorphin repressed both BMP and TGFβ signaling and was found to be toxic to primary myoblast cell cultures. In contrast, Noggin was found to be a potent and selective BMP inhibitor and was therefore tested in vivo in a DMD mouse model. Local adenoviral-mediated overexpression of Noggin in muscle resulted in an increased expression of the myogenic regulatory genes Myog and Myod1 and improved muscle histology. In conclusion, our results suggest that repression of BMP signaling may constitute an attractive adjunctive therapy for DMD patients.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
GsMTx4-blocked PIEZO1 channel promotes myogenic differentiation and alleviates myofiber damage in Duchenne muscular dystrophy.Skelet Muscle. 2025 May 14;15(1):13. doi: 10.1186/s13395-025-00383-5. Skelet Muscle. 2025. PMID: 40361216 Free PMC article.
-
Pannexin 1 dysregulation in Duchenne muscular dystrophy and its exacerbation of dystrophic features in mdx mice.Skelet Muscle. 2024 Apr 26;14(1):8. doi: 10.1186/s13395-024-00340-8. Skelet Muscle. 2024. PMID: 38671506 Free PMC article.
-
BMP4 inhibits myogenic differentiation of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells in mdx mice.Cytotherapy. 2015 Sep;17(9):1213-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jcyt.2015.06.010. Cytotherapy. 2015. PMID: 26276004
-
Sertoli Cells Improve Myogenic Differentiation, Reduce Fibrogenic Markers, and Induce Utrophin Expression in Human DMD Myoblasts.Biomolecules. 2021 Oct 12;11(10):1504. doi: 10.3390/biom11101504. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34680138 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of full-length dystrophin expression results in major cell-autonomous abnormalities in proliferating myoblasts.Elife. 2022 Sep 27;11:e75521. doi: 10.7554/eLife.75521. Elife. 2022. PMID: 36164827 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
New function of the myostatin/activin type I receptor (ALK4) as a mediator of muscle atrophy and muscle regeneration.FASEB J. 2017 Jan;31(1):238-255. doi: 10.1096/fj.201600675R. Epub 2016 Oct 12. FASEB J. 2017. PMID: 27733450 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery, synthesis and characterization of a series of 7-aryl-imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine-3-ylquinolines as activin-like kinase (ALK) inhibitors.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2020 Sep 15;30(18):127418. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2020.127418. Epub 2020 Jul 17. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2020. PMID: 32750526 Free PMC article.
-
A new class of small molecule inhibitor of BMP signaling.PLoS One. 2013 Apr 30;8(4):e62721. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0062721. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23646137 Free PMC article.
-
BMP4 and Wnt signaling interact to promote mouse tracheal mesenchyme morphogenesis.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2022 Feb 1;322(2):L224-L242. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00255.2021. Epub 2021 Dec 1. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2022. PMID: 34851738 Free PMC article.
-
Antisense-oligonucleotide mediated exon skipping in activin-receptor-like kinase 2: inhibiting the receptor that is overactive in fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva.PLoS One. 2013 Jul 4;8(7):e69096. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0069096. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23861958 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aartsma-Rus A, Bremmer-Bout M, Janson AA, den Dunnen JT, van Ommen GJ, van Deutekom JC. Targeted exon skipping as a potential gene correction therapy for Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Neuromuscul Disord. 2002;12(Suppl 1):S71–S77. - PubMed
-
- Aartsma-Rus A, Janson AA, Kaman WE, Bremmer-Bout M, den Dunnen JT, Baas F, van Ommen GJ, van Deutekom JC. Therapeutic antisense-induced exon skipping in cultured muscle cells from six different DMD patients. Hum Mol Genet. 2003;12:907–914. - PubMed
-
- Balemans W, Van Hul HW. Extracellular regulation of BMP signaling in vertebrates: a cocktail of modulators. Dev Biol. 2002;250:231–250. - PubMed
-
- Bernasconi P, Torchiana E, Confalonieri P, Brugnoni R, Barresi R, Mora M, Cornelio F, Morandi L, Mantegazza R. Expression of transforming growth factor-beta 1 in dystrophic patient muscles correlates with fibrosis. Pathogenetic role of a fibrogenic cytokine. J Clin Invest. 1995;96:1137–1144. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

