Selective knockdown of ceramide synthases reveals complex interregulation of sphingolipid metabolism
- PMID: 20940143
- PMCID: PMC2999923
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.M009142
Selective knockdown of ceramide synthases reveals complex interregulation of sphingolipid metabolism
Abstract
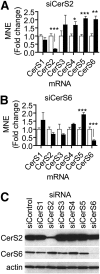
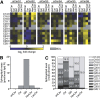
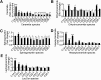
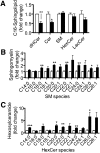
Mammalian ceramide synthases 1 to 6 (CerS1-6) generate Cer in an acyl-CoA-dependent manner, and expression of individual CerS has been shown to enhance the synthesis of ceramides with particular acyl chain lengths. However, the contribution of each CerS to steady-state levels of specific Cer species has not been evaluated. We investigated the knockdown of individual CerS in the MCF-7 human breast adenocarcinoma cell line by using small-interfering RNA (siRNA). We found that siRNA-induced downregulation of each CerS resulted in counter-regulation of nontargeted CerS. Additionally, each CerS knockdown produced unique effects on the levels of multiple sphingolipid species. For example, downregulation of CerS2 decreased very long-chain Cer but increased levels of CerS4, CerS5, and CerS6 expression and upregulated long-chain and medium-long-chain sphingolipids. Conversely, CerS6 knockdown decreased C16:0-Cer but increased CerS5 expression and caused non-C16:0 sphingolipids to be upregulated. Knockdown of individual CerS failed to decrease total sphingolipids or upregulate sphingoid bases. Treatment with siRNAs targeting combined CerS, CerS2, CerS5, and CerS6, did not change overall Cer or sphingomyelin mass but caused upregulation of dihydroceramide and hexosyl-ceramide and promoted endoplasmic reticulum stress. These data suggest that sphingolipid metabolism is robustly regulated by both redundancy in CerS-mediated Cer synthesis and counter-regulation of CerS expression.
Figures


References
-
- Hannun Y. A., Obeid L. M. 2008. Principles of bioactive lipid signalling: lessons from sphingolipids. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 9: 139–150. - PubMed
-
- Zheng W., Kollmeyer J., Symolon H., Momin A., Munter E., Wang E., Kelly S., Allegood J. C., Liu Y., Peng Q., et al. 2006. Ceramides and other bioactive sphingolipid backbones in health and disease: lipidomic analysis, metabolism and roles in membrane structure, dynamics, signaling and autophagy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1758: 1864–1884. - PubMed
-
- Sribney M. 1966. Enzymatic synthesis of ceramide. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 125: 542–547. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

