High-energy phosphotransfer in the failing mouse heart: role of adenylate kinase and glycolytic enzymes
- PMID: 20940173
- PMCID: PMC2990411
- DOI: 10.1093/eurjhf/hfq174
High-energy phosphotransfer in the failing mouse heart: role of adenylate kinase and glycolytic enzymes
Abstract
Aims: To measure the activity of the key phosphotransfer enzymes creatine kinase (CK), adenylate kinase (AK), and glycolytic enzymes in two common mouse models of chronic heart failure.
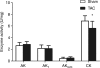
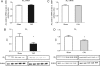
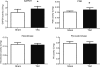
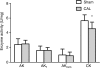
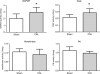
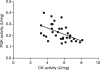
Methods and results: C57BL/6 mice were subjected to transverse aortic constriction (TAC), myocardial infarction induced by coronary artery ligation (CAL), or sham operation. Activities of phosphotransfer enzymes CK, AK, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH), 3-phosphoglycerate kinase (PGK), and pyruvate kinase were assessed spectrophotometrically. Mice were characterized by echocardiography or magnetic resonance imaging 5- to 8-week post-surgery and selected for the presence of congestive heart failure. All mice had severe left ventricular hypertrophy, impaired systolic function and pulmonary congestion compared with sham controls. A significant decrease in myocardial CK and maximal CK reaction velocity was observed in both experimental models of heart failure. However, the activity of AK and its isoforms remained unchanged, despite a reduction in its protein expression. In contrast, the activities of glycolytic phosphotransfer mediators GAPDH and PGK were 19 and 12% higher in TAC, and 31 and 23% higher in CAL models, respectively.
Conclusion: Chronic heart failure in the mouse is characterized by impaired CK function, unaltered AK, and increased activity of glycolytic phosphotransfer enzymes. This pattern of altered phosphotransfer activity was observed independent of the heart failure aetiology.
Figures
Comment in
-
On energy circuits in the failing myocardium.Eur J Heart Fail. 2010 Dec;12(12):1268-70. doi: 10.1093/eurjhf/hfq193. Eur J Heart Fail. 2010. PMID: 21098578 No abstract available.
References
-
- Laser A, Ingwall JS, Tian R, Reis I, Hu K, Gaudron P, Ertl G, Neubauer S. Regional biochemical remodeling in non-infarcted tissue of rat heart post-myocardial infarction. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1996;28:1531–1538. - PubMed
-
- Neubauer S, Frank M, Hu K, Remkes H, Laser A, Horn M, Ertl G, Lohse MJ. Changes of creatine kinase gene expression in rat heart post-myocardial infarction. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1998;30:803–810. - PubMed
-
- Lygate CA, Fischer A, Sebag-Montefiore L, Wallis J, ten Hove M, Neubauer S. The creatine kinase energy transport system in the failing mouse heart. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2007;42:1129–1136. - PubMed
-
- Neubauer S, Horn M, Cramer M, Harre K, Newell JB, Peters W, Pabst T, Ertl G, Hahn D, Ingwall JS, Kochsiek K. Myocardial phosphocreatine-to-ATP ratio is a predictor of mortality in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy. Circulation. 1997;96:2190–2196. ISSN: 0009-7322. - PubMed
-
- ten Hove M, Lygate CA, Fischer A, Schneider JE, Sang AE, Hulbert K, Sebag-Montefiore L, Watkins H, Clarke K, Isbrandt D, Wallis J, Neubauer S. Reduced inotropic reserve and increased susceptibility to cardiac ischemia/reperfusion injury in phosphocreatine-deficient guanidinoacetate-N-methyltransferase-knockout mice. Circulation. 2005;111:2477–2485. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

