Energy landscapes as a tool to integrate GPCR structure, dynamics, and function
- PMID: 20940434
- PMCID: PMC3056154
- DOI: 10.1152/physiol.00002.2010
Energy landscapes as a tool to integrate GPCR structure, dynamics, and function
Abstract
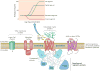
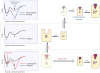
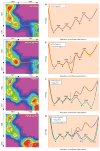
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) are versatile signaling molecules that mediate the majority of physiological responses to hormones and neurotransmitters. Recent high-resolution structural insights into GPCR structure and dynamics are beginning to shed light on the molecular basis of this versatility. We use energy landscapes to conceptualize the link between structure and function.
Figures

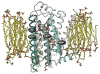
References
-
- Ballesteros JA, Jensen AD, Liapakis G, Rasmussen SG, Shi L, Gether U, Javitch JA. Activation of the beta 2-adrenergic receptor involves disruption of an ionic lock between the cytoplasmic ends of transmembrane segments 3 and 6. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:29171–29177. - PubMed
-
- Ballesteros JA, Weinstein H. Integrated methods for the construction of three dimensional models and computational probing of structure function relations in G protein-coupled receptors. In: Sealfon SC, Conn PM, editors. Methods in Neurosciences. San Diego, CA: Academic Press; 1995. pp. 366–428.
-
- Bartl FJ, Vogel R. Structural and functional properties of metarhodopsin III: recent spectroscopic studies on deactivation pathways of rhodopsin. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2007;9:1648–1658. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

