Can physical stress be measured in urine using the parameter antioxidative potential?
- PMID: 20941343
- PMCID: PMC2951104
- DOI: 10.3205/dgkh000146
Can physical stress be measured in urine using the parameter antioxidative potential?
Abstract
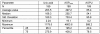
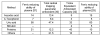
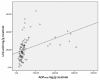
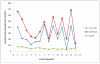
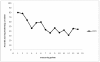
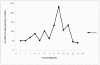
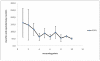
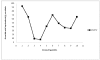
Although regular exercise is known to promote health, it is also well known that competetive sports can lead to an increase of free radical production, and thus to a drop in antioxidative potential. Thus, the present study examined the effect of competetive sports on the antioxidative potential (AOP). Using chemoluminescence, the AOP was measured in the spontaneous urine of leisure and semi-professional athletes during a training camp. Further, the parameters creatinin and uric acid were measured. It was shown that physical stress led to a drop in the antioxidant potential of up to approximately 50%. To compensate for this decline, special antioxidant food is recommended.
Regelmäßige sportliche Betätigung ist eine gesundheitsfördernde Maßnahme. Dagegen kann Leistungssport auf Grund der hohen körperlichen Belastung zu vermehrter Freisetzung von Radikalen und damit zum Abfall des antioxidativen Potentials führen. In der vorliegenden Studie sollte daher die Auswirkung von Sport auf das Antioxidative Potential (AOP) untersucht werden.
Das AOP wurde im Spontanurin von Freizeitsportlern und Leistungssportlern jeweils während eines Trainingslagers mit Hilfe der Chemolumineszenz gemessen. Weiterhin wurden die Parameter Kreatinin und Harnsäure erfasst.
Es konnte nachgewiesen werden, dass eine stärkere körperliche Belastung zu einem Abfall des antioxidativen Potentials um bis zu etwa 50% führt. Zur Kompensation erscheint eine spezielle antioxidative Kost sinnvoll.
Keywords: antioxidant capacity; antioxidant potential; physical stress; radicals; sports.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Oxidative stress and antioxidant status response of handball athletes: implications for sport training monitoring.Int Immunopharmacol. 2013 Oct;17(2):462-70. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2013.07.009. Epub 2013 Jul 31. Int Immunopharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23916597
-
Comparison of the antioxidant potential in urine, saliva and skin.GMS Krankenhhyg Interdiszip. 2011;6(1):Doc02. doi: 10.3205/dgkh000159. Epub 2011 Dec 15. GMS Krankenhhyg Interdiszip. 2011. PMID: 22242083 Free PMC article.
-
Exercise and oxidative stress: potential effects of antioxidant dietary strategies in sports.Nutrition. 2015 Jul-Aug;31(7-8):916-22. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2015.02.005. Epub 2015 Feb 19. Nutrition. 2015. PMID: 26059364 Review.
-
Oxidative stress and antioxidants in athletes undertaking regular exercise training.Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab. 2005 Apr;15(2):131-46. doi: 10.1123/ijsnem.15.2.131. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab. 2005. PMID: 16089272
-
[Exploiting dietary supplements with antioxidant properties for enhancing physical efficiency at the state of physical fatigue in sports].Vopr Pitan. 2020;89(3):86-96. doi: 10.24411/0042-8833-2020-10032. Epub 2020 May 18. Vopr Pitan. 2020. PMID: 32790261 Review. Russian.
Cited by
-
Investigating the Mutagenicity of a Cold Argon-Plasma Jet in an HET-MN Model.PLoS One. 2016 Sep 1;11(9):e0160667. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0160667. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27584003 Free PMC article.
-
Salivary and Urinary Total Antioxidant Capacity as Biomarkers of Oxidative Stress in Humans.Patholog Res Int. 2016;2016:5480267. doi: 10.1155/2016/5480267. Epub 2016 Feb 7. Patholog Res Int. 2016. PMID: 26966611 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Measurement and Clinical Significance of Biomarkers of Oxidative Stress in Humans.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017;2017:6501046. doi: 10.1155/2017/6501046. Epub 2017 Jun 18. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017. PMID: 28698768 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Altered oxidative stress and antioxidant biomarkers concentrations in pregnant individuals exposed to oil and gas sites in Northeastern British Columbia.Toxicol Sci. 2024 Sep 1;201(1):73-84. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfae080. Toxicol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38897649 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jackson MJ. An overview of methods for assessment of free radical activity in biology. Proc Nutr Soc. 1999;58(4):1001–1006. doi: 10.1017/S0029665199001317. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1017/S0029665199001317. - DOI - DOI - PubMed
-
- Halliwell B. Biochemistry of oxidative stress. Biochem Soc Trans. 2007;35(Pt 5):1147–1150. doi: 10.1042/BST0351147. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1042/BST0351147. - DOI - DOI - PubMed
-
- Borunov EV, Smirnova LP, Shchepetkin IA, Lankin VZ, Vasil'ev NV. Vysokaia aktivnost' antioksidantnykh fermentov v opukholi kak faktor “izbeganiia kontrolia” immunnoi sistemy. High activity of antioxidant enzymes in a tumor as a factor of “avoidance of control” in the immune system. Biull Eksp Biol Med. 1989;107(4):467–469. - PubMed
-
- Grimble RF. Effect of antioxidative vitamins on immune function with clinical applications. Int J Vitam Nutr Res. 1997;67(5):312–320. - PubMed
-
- Seidel C, Boehm V, Vogelsang H, Wagner A, Persin C, Glei M, Pool-Zobel BL, Jahreis G. Influence of prebiotics and antioxidants in bread on the immune system, antioxidative status and antioxidative capacity in male smokers and non-smokers. Br J Nutr. 2007;97(2):349–356. doi: 10.1017/S0007114507328626. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1017/S0007114507328626. - DOI - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

