Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-3 (TIMP-3) regulates hematopoiesis and bone formation in vivo
- PMID: 20941363
- PMCID: PMC2948005
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0013086
Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-3 (TIMP-3) regulates hematopoiesis and bone formation in vivo
Abstract
Background: Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-3 (TIMP-3) inhibits matrix metalloproteinases and membrane-bound sheddases. TIMP-3 is associated with the extracellular matrix and is expressed in highly remodeling tissues. TIMP-3 function in the hematopoietic system is unknown.
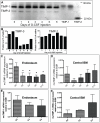
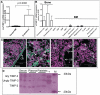
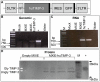
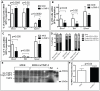
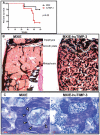
Methodology/principal findings: We now report that TIMP-3 is highly expressed in the endosteal region of the bone marrow (BM), particularly by osteoblasts, endothelial and multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells which are all important cellular components of hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) niches, whereas its expression is very low in mature leukocytes and hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells. A possible role of TIMP-3 as an important niche component was further suggested by its down-regulation during granulocyte colony-stimulating factor-induced mobilization. To further investigate TIMP-3 function, mouse HSC were retrovirally transduced with human TIMP-3 and transplanted into lethally irradiated recipients. TIMP-3 overexpression resulted in decreased frequency of B and T lymphocytes and increased frequency of myeloid cells in blood and BM, increased Lineage-negative Sca-1(+)KIT(+) cell proliferation in vivo and in vitro and increased colony-forming cell trafficking to blood and spleen. Finally, over-expression of human TIMP-3 caused a late onset fatal osteosclerosis.
Conclusions/significance: Our results suggest that TIMP-3 regulates HSC proliferation, differentiation and trafficking in vivo, as well as bone and bone turn-over, and that TIMP-3 is expressed by stromal cells forming HSC niches within the BM. Thus, TIMP-3 may be an important HSC niche component regulating both hematopoiesis and bone remodeling.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
TIMP-3 recruits quiescent hematopoietic stem cells into active cell cycle and expands multipotent progenitor pool.Blood. 2010 Nov 25;116(22):4474-82. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-01-266528. Epub 2010 Aug 26. Blood. 2010. PMID: 20798233
-
Molecular signature and in vivo behavior of bone marrow endosteal and subendosteal stromal cell populations and their relevance to hematopoiesis.Exp Cell Res. 2012 Nov 15;318(19):2427-37. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2012.07.009. Epub 2012 Jul 27. Exp Cell Res. 2012. PMID: 22841688 Free PMC article.
-
Stable colony-stimulating factor 1 fusion protein treatment increases hematopoietic stem cell pool and enhances their mobilisation in mice.J Hematol Oncol. 2021 Jan 6;14(1):3. doi: 10.1186/s13045-020-00997-w. J Hematol Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33402221 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of hematopoiesis in endosteal microenvironments.Int J Hematol. 2014 Jun;99(6):679-84. doi: 10.1007/s12185-014-1583-1. Epub 2014 Apr 24. Int J Hematol. 2014. PMID: 24760425 Review.
-
Extravascular coagulation in hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell regulation.Blood. 2018 Jul 12;132(2):123-131. doi: 10.1182/blood-2017-12-768986. Epub 2018 Jun 4. Blood. 2018. PMID: 29866813 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of Rosavin in the Pathophysiology of Bone Metabolism.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 9;25(4):2117. doi: 10.3390/ijms25042117. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38396794 Free PMC article. Review.
-
B-lymphopoiesis is stopped by mobilizing doses of G-CSF and is rescued by overexpression of the anti-apoptotic protein Bcl2.Haematologica. 2013 Mar;98(3):325-33. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2012.069260. Epub 2012 Aug 28. Haematologica. 2013. PMID: 22929978 Free PMC article.
-
The extracellular matrix of hematopoietic stem cell niches.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2022 Feb;181:114069. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2021.114069. Epub 2021 Nov 25. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2022. PMID: 34838648 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vascular niche E-selectin regulates hematopoietic stem cell dormancy, self renewal and chemoresistance.Nat Med. 2012 Nov;18(11):1651-7. doi: 10.1038/nm.2969. Epub 2012 Oct 21. Nat Med. 2012. PMID: 23086476
-
HIF-1α is required for hematopoietic stem cell mobilization and 4-prolyl hydroxylase inhibitors enhance mobilization by stabilizing HIF-1α.Leukemia. 2015 Jun;29(6):1366-78. doi: 10.1038/leu.2015.8. Epub 2015 Jan 12. Leukemia. 2015. PMID: 25578474 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nilsson SK, Johnston HM, Coverdale JA. Spatial localization of transplanted hemopoietic stem cells: inferences for the localization of stem cell niches. Blood. 2001;97:2293–2299. - PubMed
-
- Xie Y, Yin T, Wiegraebe W, He XC, Miller D, et al. Detection of functional haematopoietic stem cell niche using real-time imaging. Nature. 2009;457:97–101. - PubMed
-
- Nakamura Y, Arai F, Iwasaki H, Hosokawa K, Kobayashi I, et al. Isolation and characterization of endosteal niche cell populations that regulate hematopoietic stem cells. Blood 2010 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

