Antiretroviral treatment for children with peripartum nevirapine exposure
- PMID: 20942667
- PMCID: PMC3021781
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1000931
Antiretroviral treatment for children with peripartum nevirapine exposure
Abstract
Background: Single-dose nevirapine is the cornerstone of the regimen for prevention of mother-to-child transmission of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) in resource-limited settings, but nevirapine frequently selects for resistant virus in mothers and children who become infected despite prophylaxis. The optimal antiretroviral treatment strategy for children who have had prior exposure to single-dose nevirapine is unknown.
Methods: We conducted a randomized trial of initial therapy with zidovudine and lamivudine plus either nevirapine or ritonavir-boosted lopinavir in HIV-infected children 6 to 36 months of age, in six African countries, who qualified for treatment according to World Health Organization (WHO) criteria. Results are reported for the cohort that included children exposed to single-dose nevirapine prophylaxis. The primary end point was virologic failure or discontinuation of treatment by study week 24. Enrollment in this cohort was terminated early on the recommendation of the data and safety monitoring board.
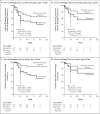
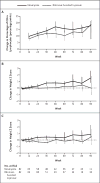
Results: A total of 164 children were enrolled. The median percentage of CD4+ lymphocytes was 19%; a total of 56% of the children had WHO stage 3 or 4 disease. More children in the nevirapine group than in the ritonavir-boosted lopinavir group reached a primary end point (39.6% vs. 21.7%; weighted difference, 18.6 percentage-points; 95% confidence interval, 3.7 to 33.6; nominal P=0.02). Baseline resistance to nevirapine was detected in 18 of 148 children (12%) and was predictive of treatment failure. No significant between-group differences were seen in the rate of adverse events.
Conclusions: Among children with prior exposure to single-dose nevirapine for perinatal prevention of HIV transmission, antiretroviral treatment consisting of zidovudine and lamivudine plus ritonavir-boosted lopinavir resulted in better outcomes than did treatment with zidovudine and lamivudine plus nevirapine. Since nevirapine is used for both treatment and perinatal prevention of HIV infection in resource-limited settings, alternative strategies for the prevention of HIV transmission from mother to child, as well as for the treatment of HIV infection, are urgently required. (Funded by the National Institutes of Health; ClinicalTrials.gov number, NCT00307151.).
Figures

Comment in
-
Preventing mother-to-child transmission of HIV—protecting this generation and the next.N Engl J Med. 2010 Oct 14;363(16):1570-2. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe1009863. N Engl J Med. 2010. PMID: 20942674 No abstract available.
References
-
- Lallemant M, Jourdain G, Le Coeur S, et al. A trial of shortened zidovudine regimens to prevent mother-to-child transmission of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. N Engl J Med. 2000;343:982–91. - PubMed
-
- Musoke P, Guay LA, Bagenda D, et al. A phase I/II study of the safety and pharmacokinetics of nevirapine in HIV-1-infected pregnant Ugandan women and their neonates (HIVNET 006) AIDS. 1999;13:479–86. - PubMed
-
- Mirochnick M, Siminski S, Fenton T, Lugo M, Sullivan JL. Nevirapine pharmacokinetics in pregnant women and in their infants after in utero exposure. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2001;20:803–5. - PubMed
-
- Cressey TR, Jourdain G, Lallemant MJ, et al. Persistence of nevirapine exposure during the postpartum period after intrapartum single-dose nevirapine in addition to zidovudine prophylaxis for the prevention of mother-to-child transmission of HIV-1. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2005;38:283–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
