Involvement of EupR, a response regulator of the NarL/FixJ family, in the control of the uptake of the compatible solutes ectoines by the halophilic bacterium Chromohalobacter salexigens
- PMID: 20942908
- PMCID: PMC2964678
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2180-10-256
Involvement of EupR, a response regulator of the NarL/FixJ family, in the control of the uptake of the compatible solutes ectoines by the halophilic bacterium Chromohalobacter salexigens
Abstract
Background: Osmosensing and associated signal transduction pathways have not yet been described in obligately halophilic bacteria. Chromohalobacter salexigens is a halophilic bacterium with a broad range of salt tolerance. In response to osmotic stress, it synthesizes and accumulates large amounts of the compatible solutes ectoine and hydroxyectoine. In a previous work, we showed that ectoines can be also accumulated upon transport from the external medium, and that they can be used as carbon sources at optimal, but not at low salinity. This was related to an insufficient ectoine(s) transport under these conditions.
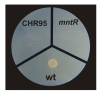
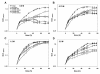
Results: A C. salexigens Tn1732-induced mutant (CHR95) showed a delayed growth with glucose at low and optimal salinities, could not grow at high salinity, and was able to use ectoines as carbon sources at low salinity. CHR95 was affected in the transport and/or metabolism of glucose, and showed a deregulated ectoine uptake at any salinity, but it was not affected in ectoine metabolism. Transposon insertion in CHR95 caused deletion of three genes, Csal0865-Csal0867: acs, encoding an acetyl-CoA synthase, mntR, encoding a transcriptional regulator of the DtxR/MntR family, and eupR, encoding a putative two-component response regulator with a LuxR_C-like DNA-binding helix-turn-helix domain. A single mntR mutant was sensitive to manganese, suggesting that mntR encodes a manganese-dependent transcriptional regulator. Deletion of eupR led to salt-sensitivity and enabled the mutant strain to use ectoines as carbon source at low salinity. Domain analysis included EupR as a member of the NarL/FixJ family of two component response regulators. Finally, the protein encoded by Csal869, located three genes downstream of eupR was suggested to be the cognate histidine kinase of EupR. This protein was predicted to be a hybrid histidine kinase with one transmembrane and one cytoplasmic sensor domain.
Conclusions: This work represents the first example of the involvement of a two-component response regulator in the osmoadaptation of a true halophilic bacterium. Our results pave the way to the elucidation of the signal transduction pathway involved in the control of ectoine transport in C. salexigens.
Figures


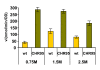

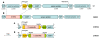
Similar articles
-
Insights into metabolic osmoadaptation of the ectoines-producer bacterium Chromohalobacter salexigens through a high-quality genome scale metabolic model.Microb Cell Fact. 2018 Jan 9;17(1):2. doi: 10.1186/s12934-017-0852-0. Microb Cell Fact. 2018. PMID: 29316921 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding the interplay of carbon and nitrogen supply for ectoines production and metabolic overflow in high density cultures of Chromohalobacter salexigens.Microb Cell Fact. 2017 Feb 8;16(1):23. doi: 10.1186/s12934-017-0643-7. Microb Cell Fact. 2017. PMID: 28179004 Free PMC article.
-
Role of central metabolism in the osmoadaptation of the halophilic bacterium Chromohalobacter salexigens.J Biol Chem. 2013 Jun 14;288(24):17769-81. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.470567. Epub 2013 Apr 24. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23615905 Free PMC article.
-
Microbial production of ectoine and hydroxyectoine as high-value chemicals.Microb Cell Fact. 2021 Mar 26;20(1):76. doi: 10.1186/s12934-021-01567-6. Microb Cell Fact. 2021. PMID: 33771157 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The ups and downs of ectoine: structural enzymology of a major microbial stress protectant and versatile nutrient.Biol Chem. 2020 Nov 26;401(12):1443-1468. doi: 10.1515/hsz-2020-0223. Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32755967 Review.
Cited by
-
A halophilic Chromohalobacter species from estuarine coastal waters as a detoxifier of manganese, as well as a novel bio-catalyst for synthesis of n-butyl acetate.Front Microbiol. 2023 Apr 12;14:1159018. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1159018. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37125204 Free PMC article.
-
A genome-wide study of two-component signal transduction systems in eight newly sequenced mutans streptococci strains.BMC Genomics. 2012 Apr 4;13:128. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-128. BMC Genomics. 2012. PMID: 22475007 Free PMC article.
-
Establishment of a markerless gene deletion system in Chromohalobacter salexigens DSM 3043.Extremophiles. 2017 Sep;21(5):839-850. doi: 10.1007/s00792-017-0946-y. Epub 2017 Jun 28. Extremophiles. 2017. PMID: 28660361
-
Comparative Transcriptomics of Cold Growth and Adaptive Features of a Eury- and Steno-Psychrophile.Front Microbiol. 2018 Jul 31;9:1565. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.01565. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30108551 Free PMC article.
-
Ectoine and hydroxyectoine as protectants against osmotic and cold stress: uptake through the SigB-controlled betaine-choline- carnitine transporter-type carrier EctT from Virgibacillus pantothenticus.J Bacteriol. 2011 Sep;193(18):4699-708. doi: 10.1128/JB.05270-11. Epub 2011 Jul 15. J Bacteriol. 2011. PMID: 21764932 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bremer E, Krämer R. In: Bacterial Stress Responses. Storz G, Hengge-Aronis R, editor. Washington DC: ASM Press; 2000. Coping with osmotic challenges: osmoregulation trough accumulation and release of compatible solutes in bacteria; pp. 79–97.
-
- Galinski EA, Trüper HG. Microbial behaviour in salt-stressed ecosystems. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1994;15:95–108. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.1994.tb00128.x. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

