Marked potentiation of cell swelling by cytokines in ammonia-sensitized cultured astrocytes
- PMID: 20942959
- PMCID: PMC2964656
- DOI: 10.1186/1742-2094-7-66
Marked potentiation of cell swelling by cytokines in ammonia-sensitized cultured astrocytes
Abstract
Background: Brain edema leading to high intracranial pressure is a lethal complication of acute liver failure (ALF), which is believed to be cytotoxic due to swelling of astrocytes. In addition to the traditional view that elevated levels of blood and brain ammonia are involved in the mechanism of brain edema in ALF, emerging evidence suggests that inflammatory cytokines also contribute to this process. We earlier reported that treatment of astrocyte cultures with a pathophysiological concentration of ammonia (5 mM NH4Cl) resulted in the activation of nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-κB) and that inhibition of such activation diminished astrocyte swelling, suggesting a key role of NF-κB in the mechanism of ammonia-induced astrocyte swelling. Since cytokines are also well-known to activate NF-κB, this study examined for additive/synergistic effects of ammonia and cytokines in the activation of NF-κB and their role in astrocyte swelling.
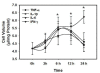
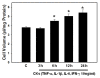
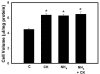
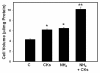
Methods: Primary cultures of astrocytes were treated with ammonia and cytokines (TNF-α, IL-1, IL-6, IFN-γ, each at 10 ng/ml), individually or in combination, and cell volume was determined by the [3H]-O-methylglucose equilibration method. The effect of ammonia and cytokines on the activation of NF-κB was determined by immunoblots.
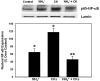
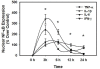
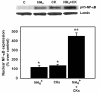
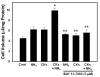
Results: Cell swelling was increased by ammonia (43%) and by cytokines (37%) at 24 h. Simultaneous co-treatment with cytokines and ammonia showed no additional swelling. By contrast, cultures pretreated with ammonia for 24 h and then exposed to cytokines for an additional 24 h, showed a marked increase in astrocyte swelling (129%). Treatment of cultures with ammonia or cytokines alone also activated NF-κB (80-130%), while co-treatment had no additive effect. However, in cultures pre-treated with ammonia for 24 h, cytokines induced a marked activation of NF-κB (428%). BAY 11-7082, an inhibitor of NF-κB, completely blocked the astrocyte swelling in cultures pre-treated with ammonia and followed by the addition of a mixture of cytokines.
Conclusion: Our results indicate that ammonia and a mixture of cytokines each cause astrocyte swelling but when these agents are added simultaneously, no additive effects were found. On the other hand, when cells were initially treated with ammonia and 24 h later given a mixture of cytokines, a marked potentiation in cell swelling and NF-κB activation occurred. These data suggest that the potentiation in cell swelling is a consequence of the initial activation of NF-κB by ammonia. These findings provide a likely mechanism for the exacerbation of brain edema in patients with ALF in the setting of sepsis/inflammation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ammonia-induced activation of p53 in cultured astrocytes: role in cell swelling and glutamate uptake.Neurochem Int. 2009 Jul-Aug;55(1-3):98-105. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2008.12.022. Epub 2009 Feb 11. Neurochem Int. 2009. PMID: 19428812
-
NF-κB in the mechanism of brain edema in acute liver failure: studies in transgenic mice.Neurobiol Dis. 2011 Feb;41(2):498-507. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2010.10.021. Epub 2010 Nov 16. Neurobiol Dis. 2011. PMID: 21087666 Free PMC article.
-
Sulfonylurea receptor 1 contributes to the astrocyte swelling and brain edema in acute liver failure.Transl Stroke Res. 2014 Feb;5(1):28-37. doi: 10.1007/s12975-014-0328-z. Epub 2014 Jan 18. Transl Stroke Res. 2014. PMID: 24443056 Free PMC article.
-
Brain edema in acute liver failure: mechanisms and concepts.Metab Brain Dis. 2014 Dec;29(4):927-36. doi: 10.1007/s11011-014-9502-y. Epub 2014 Feb 25. Metab Brain Dis. 2014. PMID: 24567229 Review.
-
New concepts in the mechanism of ammonia-induced astrocyte swelling.Metab Brain Dis. 2007 Dec;22(3-4):219-34. doi: 10.1007/s11011-007-9062-5. Metab Brain Dis. 2007. PMID: 17823859 Review.
Cited by
-
Ornithine phenylacetate revisited.Metab Brain Dis. 2013 Jun;28(2):327-31. doi: 10.1007/s11011-013-9391-5. Epub 2013 Mar 2. Metab Brain Dis. 2013. PMID: 23456516 Review.
-
Primary cultures of astrocytes: their value in understanding astrocytes in health and disease.Neurochem Res. 2012 Nov;37(11):2569-88. doi: 10.1007/s11064-012-0868-0. Epub 2012 Aug 28. Neurochem Res. 2012. PMID: 22926576 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Corallodiscus flabellata B. L. Burtt extract alleviates lipopolysaccharide/D-galactosamine-induced acute liver failure and brain injury by inhibiting oxidative stress, apoptosis, and inflammation.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2020 Nov;23(11):1445-1452. doi: 10.22038/ijbms.2020.45437.10567. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 33235702 Free PMC article.
-
Blood Ammonia as a Possible Etiological Agent for Alzheimer's Disease.Nutrients. 2018 May 4;10(5):564. doi: 10.3390/nu10050564. Nutrients. 2018. PMID: 29734664 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of cytokine release syndrome and neurotoxicity of CAR T-cell therapy and associated prevention and management strategies.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021 Nov 18;40(1):367. doi: 10.1186/s13046-021-02148-6. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 34794490 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

