Suppression of activity-regulated cytoskeleton-associated gene expression in the dorsal striatum attenuates extinction of cocaine-seeking
- PMID: 20942997
- PMCID: PMC3120104
- DOI: 10.1017/S1461145710001173
Suppression of activity-regulated cytoskeleton-associated gene expression in the dorsal striatum attenuates extinction of cocaine-seeking
Abstract
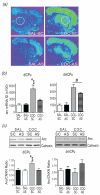
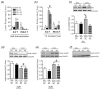
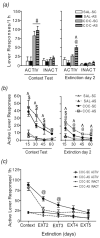
The caudate putamen (CPu) has been implicated in habit learning and neuroadaptive changes that mediate the compulsive nature of drug-seeking following chronic cocaine self-administration. Re-exposure to an operant chamber previously associated with cocaine, but not yoked-saline, increases activity-regulated cytoskeleton-associated (Arc) gene mRNA expression within the dorsolateral (dl) CPu following prolonged abstinence. In this study, we tested the hypothesis that antisense gene knockdown of Arc within the dlCPu would alter cocaine-seeking. Initial studies showed that a single infusion of Arc antisense oligodeoxynucleotide (ODN) into the dlCPu significantly attenuated the induction of Arc mRNA and Arc protein by a single cocaine exposure (20 mg/kg i.p.) compared to scrambled-ODN-infused controls. In cocaine self-administering rats, infusion of Arc antisense ODN into the dlCPu 3 h prior to a test of context-driven drug-seeking significantly attenuated Arc protein induction, but failed to alter responding during testing, suggesting striatal Arc does not facilitate context-induced drug-seeking following prolonged abstinence. However, Arc antisense ODN infusion blunted the decrease in responding during subsequent 1-h extinction tests 24 and 48 h later. Following re-exposure to a cocaine-paired context, surface expression of the AMPA-type glutamate receptor GluR1 was significantly reduced whereas GluR2 was significantly increased in the dlCPu, independent of Arc antisense ODN infusion. Together, these findings indicate an important role for Arc in neuroadaptations within brain regions responsible for drug-seeking after abstinence and direct attention to changes occurring within striatal circuitry that are necessary to break down the habitual behaviour that leads to relapse.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Relapse to cocaine-seeking increases activity-regulated gene expression differentially in the striatum and cerebral cortex of rats following short or long periods of abstinence.Brain Struct Funct. 2008 Sep;213(1-2):215-27. doi: 10.1007/s00429-008-0182-4. Epub 2008 May 17. Brain Struct Funct. 2008. PMID: 18488248 Free PMC article.
-
Dorsal striatum mediation of cocaine-seeking after withdrawal from short or long daily access cocaine self-administration in rats.Behav Brain Res. 2011 Apr 15;218(2):296-300. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2010.12.014. Epub 2010 Dec 15. Behav Brain Res. 2011. PMID: 21167212 Free PMC article.
-
Context-driven cocaine-seeking in abstinent rats increases activity-regulated gene expression in the basolateral amygdala and dorsal hippocampus differentially following short and long periods of abstinence.Neuroscience. 2010 Oct 13;170(2):570-9. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2010.07.027. Epub 2010 Jul 21. Neuroscience. 2010. PMID: 20654701 Free PMC article.
-
Extinction-induced neuroplasticity attenuates stress-induced cocaine seeking: a state-dependent learning hypothesis.Stress. 2004 Sep;7(3):145-55. doi: 10.1080/10253890400012677. Stress. 2004. PMID: 15764012 Review.
-
Extinction training regulates neuroadaptive responses to withdrawal from chronic cocaine self-administration.Learn Mem. 2004 Sep-Oct;11(5):648-57. doi: 10.1101/lm.81404. Learn Mem. 2004. PMID: 15466321 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Biogenesis, physiological functions and potential applications of extracellular vesicles in substance use disorders.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 Jun;78(11):4849-4865. doi: 10.1007/s00018-021-03824-8. Epub 2021 Apr 5. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33821293 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Choosing Money over Drugs: The Neural Underpinnings of Difficult Choice in Chronic Cocaine Users.J Addict. 2014;2014:189853. doi: 10.1155/2014/189853. Epub 2014 Aug 14. J Addict. 2014. PMID: 25197609 Free PMC article.
-
Serotonin at the nexus of impulsivity and cue reactivity in cocaine addiction.Neuropharmacology. 2014 Jan;76 Pt B(0 0):460-78. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.06.030. Epub 2013 Jul 11. Neuropharmacology. 2014. PMID: 23850573 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The activity-regulated cytoskeleton-associated protein, Arc/Arg3.1, influences mouse cocaine self-administration.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2020 Jan;188:172818. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2019.172818. Epub 2019 Nov 1. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2020. PMID: 31682894 Free PMC article.
-
Cocaine and Amphetamine Induce Overlapping but Distinct Patterns of AMPAR Plasticity in Nucleus Accumbens Medium Spiny Neurons.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2016 Jan;41(2):464-76. doi: 10.1038/npp.2015.168. Epub 2015 Jun 12. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2016. PMID: 26068728 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beattie EC, Carroll RC, Yu X, Morishita W, et al. Regulation of AMPA receptor endocytosis by a signaling mechanism shared with LTD. Nature Neuroscience. 2000;3:1291–1300. - PubMed
-
- Bliss TV, Collingridge GL. A synaptic model of memory: long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Nature. 1993;361:31–39. - PubMed
-
- Boudreau AC, Reimers JM, Milovanovic M, Wolf ME. Cell surface AMPA receptors in the rat nucleus accumbens increase during cocaine withdrawal but internalize after cocaine challenge in association with altered activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases. Journal of Neuroscience. 2007;27:10621–10635. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

