Structural and biochemical studies on the chromo-barrel domain of male specific lethal 3 (MSL3) reveal a binding preference for mono- or dimethyllysine 20 on histone H4
- PMID: 20943666
- PMCID: PMC3003388
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.134312
Structural and biochemical studies on the chromo-barrel domain of male specific lethal 3 (MSL3) reveal a binding preference for mono- or dimethyllysine 20 on histone H4
Abstract
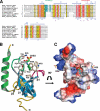
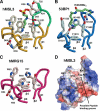
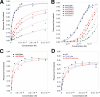
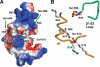
We have determined the human male specific lethal 3 (hMSL3) chromo-barrel domain structure by x-ray crystallography to a resolution of 2.5 Å (r = 0.226, R(free) = 0.270). hMSL3 contains a canonical methyllysine binding pocket made up of residues Tyr-31, Phe-56, Trp-59, and Trp-63. A six-residue insertion between strands β(1) and β(2) of the hMSL3 chromo-barrel domain directs the side chain of Glu-21 into the methyllysine binding pocket where it hydrogen bonds to the NH group of a bound cyclohexylamino ethanesulfonate buffer molecule, likely mimicking interactions with a histone tail dimethyllysine residue. In vitro binding studies revealed that both the human and Drosophila MSL3 chromo-barrel domains bind preferentially to peptides representing the mono or dimethyl isoform of lysine 20 on the histone H4 N-terminal tail (H4K20Me(1) or H4K20Me(2)). Mutation of Tyr-31 to Ala in the hMSL3 methyllysine-binding cage resulted in weaker in vitro binding to H4K20Me(1). The same mutation in the msl3 gene compromised male survival in Drosophila. Combined mutation of Glu-21 and Pro-22 to Ala in hMSL3 resulted in slightly weaker in vitro binding to H4K20Me(1), but the corresponding msl3 mutation had no effect on male survival in Drosophila. We propose MSL3 plays an important role in targeting the male specific lethal complex to chromatin in both humans and flies by binding to H4K20Me(1). Binding studies on the related dMRG15 chromo-barrel domain revealed that MRG15 prefers binding to H4K20Me(3).
Figures

Similar articles
-
Structure of human MRG15 chromo domain and its binding to Lys36-methylated histone H3.Nucleic Acids Res. 2006;34(22):6621-8. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl989. Epub 2006 Nov 28. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006. PMID: 17135209 Free PMC article.
-
The MRG domain mediates the functional integration of MSL3 into the dosage compensation complex.Mol Cell Biol. 2005 Jul;25(14):5947-54. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.14.5947-5954.2005. Mol Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15988010 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of the chromo barrel domain from the MOF acetyltransferase.J Biol Chem. 2005 Sep 16;280(37):32326-31. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M501347200. Epub 2005 Jun 17. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15964847
-
Dosage Compensation of the X Chromosome: A Complex Epigenetic Assignment Involving Chromatin Regulators and Long Noncoding RNAs.Annu Rev Biochem. 2018 Jun 20;87:323-350. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biochem-062917-011816. Epub 2018 Apr 18. Annu Rev Biochem. 2018. PMID: 29668306 Review.
-
Towards understanding methyllysine readout.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Aug;1839(8):686-93. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2014.04.001. Epub 2014 Apr 13. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 24727128 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Evolution of the Drosophila melanogaster Chromatin Landscape and Its Associated Proteins.Genome Biol Evol. 2019 Mar 1;11(3):660-677. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evz019. Genome Biol Evol. 2019. PMID: 30689829 Free PMC article.
-
Select human cancer mutants of NRMT1 alter its catalytic activity and decrease N-terminal trimethylation.Protein Sci. 2017 Aug;26(8):1639-1652. doi: 10.1002/pro.3202. Epub 2017 Jun 11. Protein Sci. 2017. PMID: 28556566 Free PMC article.
-
The many lives of KATs - detectors, integrators and modulators of the cellular environment.Nat Rev Genet. 2019 Jan;20(1):7-23. doi: 10.1038/s41576-018-0072-4. Nat Rev Genet. 2019. PMID: 30390049 Review.
-
Structure and mechanisms of lysine methylation recognition by the chromodomain in gene transcription.Biochemistry. 2011 Mar 29;50(12):1966-80. doi: 10.1021/bi101885m. Epub 2011 Feb 23. Biochemistry. 2011. PMID: 21288002 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of H3K36 methylation and associated methyltransferases in chromosome-specific gene regulation.Sci Adv. 2021 Oct;7(40):eabh4390. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abh4390. Epub 2021 Oct 1. Sci Adv. 2021. PMID: 34597135 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

