Interdependent roles for accessory KChIP2, KChIP3, and KChIP4 subunits in the generation of Kv4-encoded IA channels in cortical pyramidal neurons
- PMID: 20943905
- PMCID: PMC2993613
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2487-10.2010
Interdependent roles for accessory KChIP2, KChIP3, and KChIP4 subunits in the generation of Kv4-encoded IA channels in cortical pyramidal neurons
Abstract
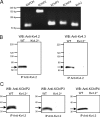
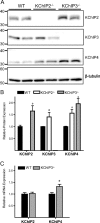
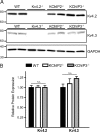
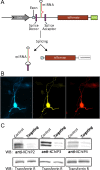
The rapidly activating and inactivating voltage-dependent outward K(+) (Kv) current, I(A), is widely expressed in central and peripheral neurons. I(A) has long been recognized to play important roles in determining neuronal firing properties and regulating neuronal excitability. Previous work demonstrated that Kv4.2 and Kv4.3 α-subunits are the primary determinants of I(A) in mouse cortical pyramidal neurons. Accumulating evidence indicates that native neuronal Kv4 channels function in macromolecular protein complexes that contain accessory subunits and other regulatory molecules. The K(+) channel interacting proteins (KChIPs) are among the identified Kv4 channel accessory subunits and are thought to be important for the formation and functioning of neuronal Kv4 channel complexes. Molecular genetic, biochemical, and electrophysiological approaches were exploited in the experiments described here to examine directly the roles of KChIPs in the generation of functional Kv4-encoded I(A) channels. These combined experiments revealed that KChIP2, KChIP3, and KChIP4 are robustly expressed in adult mouse posterior (visual) cortex and that all three proteins coimmunoprecipitate with Kv4.2. In addition, in cortical pyramidal neurons from mice lacking KChIP3 (KChIP3(-/-)), mean I(A) densities were reduced modestly, whereas in mean I(A) densities in KChIP2(-/-) and WT neurons were not significantly different. Interestingly, in both KChIP3(-/-) and KChIP2(-/-) cortices, the expression levels of the other KChIPs (KChIP2 and 4 or KChIP3 and 4, respectively) were increased. In neurons expressing constructs to mediate simultaneous RNA interference-induced reductions in the expression of KChIP2, 3, and 4, I(A) densities were markedly reduced and Kv current remodeling was evident.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Electrical remodelling maintains firing properties in cortical pyramidal neurons lacking KCND2-encoded A-type K+ currents.J Physiol. 2008 Mar 15;586(6):1565-79. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2007.146597. Epub 2008 Jan 10. J Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18187474 Free PMC article.
-
Multiprotein assembly of Kv4.2, KChIP3 and DPP10 produces ternary channel complexes with ISA-like properties.J Physiol. 2005 Nov 1;568(Pt 3):767-88. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2005.087858. Epub 2005 Aug 25. J Physiol. 2005. PMID: 16123112 Free PMC article.
-
KV Channel-Interacting Proteins in the Neurological and Cardiovascular Systems: An Updated Review.Cells. 2023 Jul 20;12(14):1894. doi: 10.3390/cells12141894. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37508558 Free PMC article. Review.
-
KChIPs and Kv4 alpha subunits as integral components of A-type potassium channels in mammalian brain.J Neurosci. 2004 Sep 8;24(36):7903-15. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0776-04.2004. J Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15356203 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological Approaches for the Modulation of the Potassium Channel KV4.x and KChIPs.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 31;22(3):1419. doi: 10.3390/ijms22031419. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33572566 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Different KChIPs compete for heteromultimeric assembly with pore-forming Kv4 subunits.Biophys J. 2015 Jun 2;108(11):2658-69. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2015.04.024. Biophys J. 2015. PMID: 26039167 Free PMC article.
-
The A-current modulates learning via NMDA receptors containing the NR2B subunit.PLoS One. 2011;6(9):e24915. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0024915. Epub 2011 Sep 26. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21966384 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of Navβ4-Mediated Regulation of Sodium Currents in Adult Purkinje Neurons Disrupts Firing and Impairs Motor Coordination and Balance.Cell Rep. 2017 Apr 18;19(3):532-544. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.03.068. Cell Rep. 2017. PMID: 28423317 Free PMC article.
-
Neuronal voltage-gated K+ (Kv) channels function in macromolecular complexes.Neurosci Lett. 2010 Dec 10;486(2):73-7. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2010.08.067. Epub 2010 Sep 9. Neurosci Lett. 2010. PMID: 20813163 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The auxiliary subunit KChIP2 is an essential regulator of homeostatic excitability.J Biol Chem. 2013 May 10;288(19):13258-68. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.434548. Epub 2013 Mar 27. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23536187 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aghajanian GK. Modulation of a transient outward current in serotonergic neurones by alpha 1-adrenoceptors. Nature. 1985;315:501–503. - PubMed
-
- Aimond F, Kwak SP, Rhodes KJ, Nerbonne JM. Accessory Kvbeta1 subunits differentially modulate the functional expression of voltage-gated K+ channels in mouse ventricular myocytes. Circ Res. 2005;96:451–458. - PubMed
-
- An WF, Bowlby MR, Betty M, Cao J, Ling HP, Mendoza G, Hinson JW, Mattsson KI, Strassle BW, Trimmer JS, Rhodes KJ. Modulation of A-type potassium channels by a family of calcium sensors. Nature. 2000;403:553–556. - PubMed
-
- Anderson D, Rehak R, Hameed SW, Hamish M, Zamponi GW, Turner RW. Regulation of the KV4.2 complex by CaV3.1 calcium channels. Channels (Austin) 2010a;4:163–167. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
