Glucocorticoids exacerbate lipopolysaccharide-induced signaling in the frontal cortex and hippocampus in a dose-dependent manner
- PMID: 20943909
- PMCID: PMC3842494
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0303-09.2010
Glucocorticoids exacerbate lipopolysaccharide-induced signaling in the frontal cortex and hippocampus in a dose-dependent manner
Abstract
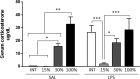
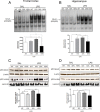
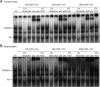
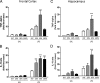
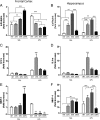
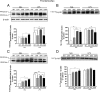
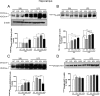
Although the anti-inflammatory actions of glucocorticoids (GCs) are well established, evidence has accumulated showing that proinflammatory GC effects can occur in the brain, in a poorly understood manner. Using electrophoretic mobility shift assay, real-time PCR, and immunoblotting, we investigated the ability of varying concentrations of corticosterone (CORT, the GC of rats) to modulate lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced activation of NF-κB (nuclear factor κB), expression of anti- and proinflammatory factors and of the MAP (mitogen-activated protein) kinase family [ERK (extracellular signal-regulated kinase), p38, and JNK/SAPK (c-Jun N-terminal protein kinase/stress-activated protein kinase)], and AKT. In the frontal cortex, elevated CORT levels were proinflammatory, exacerbating LPS effects on NF-κB, MAP kinases, and proinflammatory gene expression. Milder proinflammatory GCs effects occurred in the hippocampus. In the absence of LPS, elevated CORT levels increased basal activation of ERK1/2, p38, SAPK/JNK, and AKT in both regions. These findings suggest that GCs do not uniformly suppress neuroinflammation and can even enhance it at multiple levels in the pathway linking LPS exposure to inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no biomedical financial interests or potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Aljada A, Ghanim H, Assian E, Mohanty P, Hamouda W, Garg R, Dandona P. Increased IkappaB expression and diminished nuclear NF-kappaB in human mononuclear cells following hydrocortisone injection. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1999;84:3386–3389. - PubMed
-
- Almawi WY, Melemedjian OK. Negative regulation of nuclear factor-kappaB activation and function by glucocorticoids. J Mol Endocrinol. 2002;28:69–78. - PubMed
-
- Annane D, Sébille V, Bellissant E, Ger-Inf-05 Study Group Effect of low doses of corticosteroids in septic shock patients with or without early acute respiratory distress syndrome. Crit Care Med. 2006;34:22–30. - PubMed
-
- Beishuizen A, Thijs LG. Endotoxin and the hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis. J Endotoxin Res. 2003;9:3–24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
