REEP2 enhances sweet receptor function by recruitment to lipid rafts
- PMID: 20943918
- PMCID: PMC3168766
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0091-10.2010
REEP2 enhances sweet receptor function by recruitment to lipid rafts
Abstract
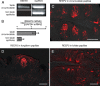
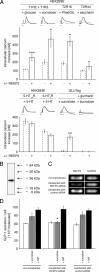
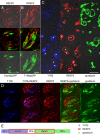
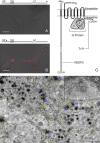
Heterologously expressed sensory receptors generally do not achieve the ligand sensitivity observed in vivo, and may require specific accessory proteins to ensure optimal function. We searched for taste cell-expressed receptor transporting protein (RTP) and receptor expression enhancing protein (REEP) family members that might serve as accessory molecules to enhance gustatory receptor function. We determined that REEP2 is an integral membrane protein expressed in taste cells, physically associates with both subunits of the type 1 taste receptor 2 and type 1 taste receptor 3 sweet receptor and specifically enhances responses to tastants of heterologously expressed sweet and bitter taste receptors. Downregulation of endogenously expressed REEP2 in the chemosensory enteroendocrine GLUTag cell line dramatically reduced sensitivity of endogenous sweet receptors. In contrast to the observation that RTP1, RTP2, and REEP1 enhance function of olfactory receptors by promoting their transit to the cell surface, we found that REEP2 does not increase cell surface expression of sweet receptors but instead alters their spatial organization. REEP2 recruits sweet receptors into lipid raft microdomains localized near the taste cell's apical region, thereby improving G-protein-coupled receptor signaling and promoting receptor access to tastants arriving through the apical taste pore.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Expression of Galpha14 in sweet-transducing taste cells of the posterior tongue.BMC Neurosci. 2008 Nov 13;9:110. doi: 10.1186/1471-2202-9-110. BMC Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 19014514 Free PMC article.
-
Regulator of G-protein signaling-21 (RGS21) is an inhibitor of bitter gustatory signaling found in lingual and airway epithelia.J Biol Chem. 2012 Dec 7;287(50):41706-19. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.423806. Epub 2012 Oct 24. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 23095746 Free PMC article.
-
Coding of sweet, bitter, and umami tastes: different receptor cells sharing similar signaling pathways.Cell. 2003 Feb 7;112(3):293-301. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(03)00071-0. Cell. 2003. PMID: 12581520
-
Taste information derived from T1R-expressing taste cells in mice.Biochem J. 2016 Mar 1;473(5):525-36. doi: 10.1042/BJ20151015. Biochem J. 2016. PMID: 26912569 Review.
-
Bitter-sweet solution in taste transduction.Cell. 2003 Feb 7;112(3):283-4. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(03)00077-1. Cell. 2003. PMID: 12581516 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring the eukaryotic Yip and REEP/Yop superfamily of membrane-shaping adapter proteins (MSAPs): A cacophony or harmony of structure and function?Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Aug 19;9:912848. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.912848. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 36060263 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CD36- and GPR120-mediated Ca²⁺ signaling in human taste bud cells mediates differential responses to fatty acids and is altered in obese mice.Gastroenterology. 2014 Apr;146(4):995-1005. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2014.01.006. Epub 2014 Jan 9. Gastroenterology. 2014. PMID: 24412488 Free PMC article.
-
BmREEPa Is a Novel Gene that Facilitates BmNPV Entry into Silkworm Cells.PLoS One. 2015 Dec 14;10(12):e0144575. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0144575. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26656276 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution of signal multiplexing by 14-3-3-binding 2R-ohnologue protein families in the vertebrates.Open Biol. 2012 Jul;2(7):120103. doi: 10.1098/rsob.120103. Open Biol. 2012. PMID: 22870394 Free PMC article.
-
REEP1 and REEP2 proteins are preferentially expressed in neuronal and neuronal-like exocytotic tissues.Brain Res. 2014 Jan 30;1545:12-22. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2013.12.008. Epub 2013 Dec 16. Brain Res. 2014. PMID: 24355597 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Behrens M, Bartelt J, Reichling C, Winnig M, Kuhn C, Meyerhof W. Members of RTP and REEP gene families influence functional bitter taste receptor expression. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:20650–20659. - PubMed
-
- Bendtsen JD, Nielsen H, von Heijne G, Brunak S. Improved prediction of signal peptides: SignalP 3.0. J Mol Biol. 2004;340:783–795. - PubMed
-
- Bodin S, Soulet C, Tronchère H, Sié P, Gachet C, Plantavid M, Payrastre B. Integrin-dependent interaction of lipid rafts with the actin cytoskeleton in activated human platelets. J Cell Sci. 2005;118:759–769. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
