Mechanisms involved in systemic nicotine-induced glutamatergic synaptic plasticity on dopamine neurons in the ventral tegmental area
- PMID: 20943922
- PMCID: PMC2995497
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1943-10.2010
Mechanisms involved in systemic nicotine-induced glutamatergic synaptic plasticity on dopamine neurons in the ventral tegmental area
Abstract
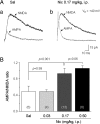
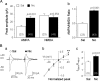
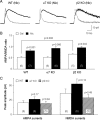
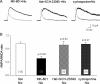
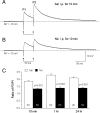
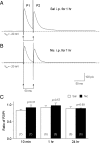
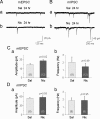
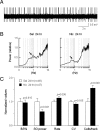
Systemic exposure to nicotine induces glutamatergic synaptic plasticity on dopamine (DA) neurons in the ventral tegmental area (VTA), but mechanisms are largely unknown. Here, we report that single, systemic exposure in rats to nicotine (0.17 mg/kg free base) increases the ratio of DA neuronal currents mediated by AMPA relative to NMDA receptors (AMPA/NMDA ratio) assessed 24 h later, based on slice-patch recording. The AMPA/NMDA ratio increase is evident within 1 h and lasts for at least 72 h after nicotine exposure (and up to 8 d after repeated nicotine administration). This effect cannot be prevented by systemic injection of either α7-nAChR (nicotinic ACh receptor)-selective [methyllycaconitine (MLA)] or β2*-nAChR-selective [mecamylamine (MEC)] antagonists but is prevented by coinjection of MLA and MEC. In either nAChR α7 or β2 subunit knock-out mice, systemic exposure to nicotine still increases the AMPA/NMDA ratio. Preinjection in rats of a NMDA receptor antagonist MK-801((+)-5-methyl-10,11-dihydro-5H-dibenzo[a,d]cyclohepten-5,10-imine maleate), but neither DA receptor antagonists [SCH-23390 (R-(+)-7-chloro-8-hydroxy-3-methyl-1-phenyl-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-1H-3-benzazepine) plus haloperidol] nor a calcineurin inhibitor (cyclosporine), prevents the nicotine-induced increase in AMPA/NMDA ratio. After systemic exposure to nicotine, glutamatergic (but not GABAergic) transmission onto rat VTA DA neuronal inputs is enhanced. Correspondingly, DA neuronal firing measured 24 h after nicotine exposure using extracellular single-unit recording in vivo is significantly faster, and there is conversion of silent to active DA neurons. Collectively, these findings demonstrate that systemic nicotine acting via either α7- or β2*-nAChRs increases presynaptic and postsynaptic glutamatergic function, and consequently initiates glutamatergic synaptic plasticity, which may be an important, early neuronal adaptation in nicotine reward and reinforcement.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Exposure of nicotine to ventral tegmental area slices induces glutamatergic synaptic plasticity on dopamine neurons.Synapse. 2011 Apr;65(4):332-8. doi: 10.1002/syn.20850. Epub 2010 Nov 11. Synapse. 2011. PMID: 20730803
-
Nicotine potentiation of excitatory inputs to ventral tegmental area dopamine neurons.J Neurosci. 2011 May 4;31(18):6710-20. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5671-10.2011. J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21543600 Free PMC article.
-
Functional nicotinic acetylcholine receptors containing α6 subunits are on GABAergic neuronal boutons adherent to ventral tegmental area dopamine neurons.J Neurosci. 2011 Feb 16;31(7):2537-48. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3003-10.2011. J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21325521 Free PMC article.
-
Age dependent nicotinic influences over dopamine neuron synaptic plasticity.Biochem Pharmacol. 2009 Oct 1;78(7):686-92. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2009.05.014. Epub 2009 May 21. Biochem Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19464268 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glutamate plasticity in the drunken amygdala: the making of an anxious synapse.Int Rev Neurobiol. 2010;91:205-33. doi: 10.1016/S0074-7742(10)91007-6. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2010. PMID: 20813244 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors: neuroplastic changes underlying alcohol and nicotine addictions.Front Mol Neurosci. 2012 Aug 3;5:83. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2012.00083. eCollection 2012. Front Mol Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22876217 Free PMC article.
-
Vezatin regulates seizures by controlling AMPAR-mediated synaptic activity.Cell Death Dis. 2021 Oct 12;12(10):936. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-04233-2. Cell Death Dis. 2021. PMID: 34642320 Free PMC article.
-
Dopamine D₂ and acetylcholine α7 nicotinic receptors have subcellular distributions favoring mediation of convergent signaling in the mouse ventral tegmental area.Neuroscience. 2013 Nov 12;252:126-43. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.08.008. Epub 2013 Aug 15. Neuroscience. 2013. PMID: 23954803 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of metabonomic for a gateway drug: nicotine priming enhances behavioral response to cocaine with modification in energy metabolism and neurotransmitter level.PLoS One. 2014 Jan 28;9(1):e87040. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0087040. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24489831 Free PMC article.
-
Dopaminergic and cholinergic learning mechanisms in nicotine addiction.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2015 Sep;1349(1):46-63. doi: 10.1111/nyas.12871. Epub 2015 Aug 24. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2015. PMID: 26301866 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bissière S, Humeau Y, Lüthi A. Dopamine gates LTP induction in lateral amygdala by suppressing feedforward inhibition. Nat Neurosci. 2003;6:587–592. - PubMed
-
- Bunney BS, Grace AA. Acute and chronic haloperidol treatment: comparison of effects on nigral dopaminergic cell activity. Life Sci. 1978;23:1715–1727. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
