AS160 associates with the Na+,K+-ATPase and mediates the adenosine monophosphate-stimulated protein kinase-dependent regulation of sodium pump surface expression
- PMID: 20943949
- PMCID: PMC3002392
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.E10-06-0507
AS160 associates with the Na+,K+-ATPase and mediates the adenosine monophosphate-stimulated protein kinase-dependent regulation of sodium pump surface expression
Abstract
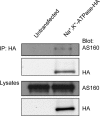
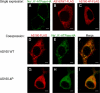
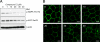
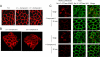
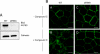
The Na(+),K(+)-ATPase is the major active transport protein found in the plasma membranes of most epithelial cell types. The regulation of Na(+),K(+)-ATPase activity involves a variety of mechanisms, including regulated endocytosis and recycling. Our efforts to identify novel Na(+),K(+)-ATPase binding partners revealed a direct association between the Na(+),K(+)-ATPase and AS160, a Rab-GTPase-activating protein. In COS cells, coexpression of AS160 and Na(+),K(+)-ATPase led to the intracellular retention of the sodium pump. We find that AS160 interacts with the large cytoplasmic NP domain of the α-subunit of the Na(+),K(+)-ATPase. Inhibition of the activity of the adenosine monophosphate-stimulated protein kinase (AMPK) in Madin-Darby canine kidney cells through treatment with Compound C induces Na(+),K(+)-ATPase endocytosis. This effect of Compound C is prevented through the short hairpin RNA-mediated knockdown of AS160, demonstrating that AMPK and AS160 participate in a common pathway to modulate the cell surface expression of the Na(+),K(+)-ATPase.
Figures


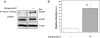
References
-
- Al-Khalili L., Kotova O., Tsuchida H., Ehren I., Feraille E., Krook A., Chibalin A. V. ERK1/2 mediates insulin stimulation of Na(+),K(+)-ATPase by phosphorylation of the alpha-subunit in human skeletal muscle cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2004;279:25211–25218. - PubMed
-
- Al-Khalili L., Yu M., Chibalin A. V. Na+,K+-ATPase trafficking in skeletal muscle: insulin stimulates translocation of both alpha 1- and alpha 2-subunit isoforms. FEBS Lett. 2003;536:198–202. - PubMed
-
- Barlet-Bas C., Khadouri C., Marsy S., Doucet A. Enhanced intracellular sodium concentration in kidney cells recruits a latent pool of Na-K-ATPase whose size is modulated by corticosteroids. J. Biol. Chem. 1990;265:7799–7803. - PubMed
-
- Bertorello A. M., Komarova Y., Smith K., Leibiger I. B., Efendiev R., Pedemonte C. H., Borisy G., Sznajder J. I. Analysis of Na+,K+-ATPase motion and incorporation into the plasma membrane in response to G protein-coupled receptor signals in living cells. Mol. Biol. Cell. 2003;14:1149–1157. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

