Identification of specific determinants of human APOBEC3F, APOBEC3C, and APOBEC3DE and African green monkey APOBEC3F that interact with HIV-1 Vif
- PMID: 20943965
- PMCID: PMC3004357
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01437-10
Identification of specific determinants of human APOBEC3F, APOBEC3C, and APOBEC3DE and African green monkey APOBEC3F that interact with HIV-1 Vif
Abstract
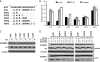
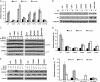
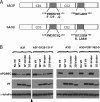
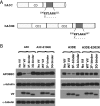
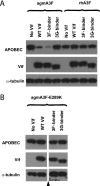
Human APOBEC3F (hA3F) and human APOBEC3G (hA3G) are potent anti-human immunodeficiency virus (anti-HIV) host factors that suppress viral replication by hypermutating the viral genome, inhibiting reverse transcription, and hindering integration. To overcome hA3F and hA3G, HIV-1 encodes Vif, which binds and targets these host proteins for proteasomal degradation. Previously, we reported that the hA3F-Vif interactions that lead to hA3F degradation are located in the region comprising amino acids 283 to 300. We have now performed mutational analysis of this region and found that the (289)EFLARH(294) amino acids contribute to hA3F-Vif binding and are critical for A3F's sensitivity to Vif. Mutants in which E289 is mutated significantly increase hA3F's ability to inhibit viral infectivity in the presence of Vif, and coimmunoprecipitation assays show that binding of Vif to the E289K mutant is decreased. We examined the role of the EFLARH sequence in other A3 proteins, including human A3C (hA3C), human A3DE (hA3DE), African green monkey A3F (agmA3F), and rhesus macaque A3F (rhA3F). hA3C, hA3DE, and agmA3F were all susceptible to degradation induced by HIV-1 Vif, while rhA3F was not. Mutagenesis of the glutamate in the EFLARH sites of hA3C, hA3DE, and agmA3F decreases the susceptibilities of these proteins to Vif-induced degradation. Together, these results indicate that the EFLARH region in hA3F, hA3C, hA3DE, and agmA3F interacts with HIV-1 Vif and that this interaction plays a role in the Vif-mediated proteasomal degradation of these A3 proteins. These studies identify a conserved region in 3 of 7 human A3 proteins that is critical for degradation mediated by HIV-1 Vif and provide structural insights into the hA3F-Vif interactions that could facilitate the development of a novel class of anti-HIV agents.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Vif Proteins from Diverse Human Immunodeficiency Virus/Simian Immunodeficiency Virus Lineages Have Distinct Binding Sites in A3C.J Virol. 2016 Oct 28;90(22):10193-10208. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01497-16. Print 2016 Nov 15. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 27581978 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct domains within APOBEC3G and APOBEC3F interact with separate regions of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Vif.J Virol. 2009 Feb;83(4):1992-2003. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01621-08. Epub 2008 Nov 26. J Virol. 2009. PMID: 19036809 Free PMC article.
-
APOBEC3G and APOBEC3F Act in Concert To Extinguish HIV-1 Replication.J Virol. 2016 Apr 14;90(9):4681-4695. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03275-15. Print 2016 May. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 26912618 Free PMC article.
-
Tumultuous relationship between the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 viral infectivity factor (Vif) and the human APOBEC-3G and APOBEC-3F restriction factors.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2009 Jun;73(2):211-32. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00040-08. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2009. PMID: 19487726 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multiple APOBEC3 restriction factors for HIV-1 and one Vif to rule them all.J Mol Biol. 2014 Mar 20;426(6):1220-45. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2013.10.033. Epub 2013 Nov 2. J Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 24189052 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Single Nucleotide Polymorphism in Human APOBEC3C Enhances Restriction of Lentiviruses.PLoS Pathog. 2016 Oct 12;12(10):e1005865. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005865. eCollection 2016 Oct. PLoS Pathog. 2016. PMID: 27732658 Free PMC article.
-
The in vitro Biochemical Characterization of an HIV-1 Restriction Factor APOBEC3F: Importance of Loop 7 on Both CD1 and CD2 for DNA Binding and Deamination.J Mol Biol. 2016 Jul 3;428(13):2661-70. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2016.03.031. Epub 2016 Apr 8. J Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 27063502 Free PMC article.
-
Lack of association between intact/deletion polymorphisms of the APOBEC3B gene and HIV-1 risk.PLoS One. 2014 Mar 25;9(3):e92861. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0092861. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24667791 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
APOBEC3D and APOBEC3F potently promote HIV-1 diversification and evolution in humanized mouse model.PLoS Pathog. 2014 Oct 16;10(10):e1004453. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004453. eCollection 2014 Oct. PLoS Pathog. 2014. PMID: 25330146 Free PMC article.
-
RNA binding to APOBEC deaminases; Not simply a substrate for C to U editing.RNA Biol. 2017 Sep 2;14(9):1153-1165. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2016.1259783. Epub 2016 Nov 21. RNA Biol. 2017. PMID: 27869537 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

