Quantitative and qualitative RNA-Seq-based evaluation of Epstein-Barr virus transcription in type I latency Burkitt's lymphoma cells
- PMID: 20943983
- PMCID: PMC3004295
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01521-10
Quantitative and qualitative RNA-Seq-based evaluation of Epstein-Barr virus transcription in type I latency Burkitt's lymphoma cells
Abstract
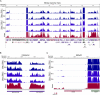
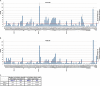
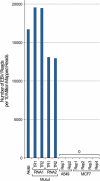
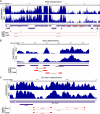
RNA-seq provides a rich source of transcriptome information with high qualitative and quantitative value. Here, we provide a pipeline for Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) transcriptome analysis using RNA-seq and we apply it to two type I latency cell lines, Mutu I and Akata. This analysis revealed substantial average expression levels of many lytic genes in predominantly latent cell populations. The lytic transcripts BHLF1 and LF3 were expressed at levels greater than those for 98% of all cellular polyadenylated transcripts. Exon junction mapping accurately identified the Qp-derived EBNA1 splicing pattern, lytic gene splicing, and a complex splicing pattern within the BamHI A region.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Interferon-γ-inducible protein 16 (IFI16) is required for the maintenance of Epstein-Barr virus latency.Virol J. 2017 Nov 13;14(1):221. doi: 10.1186/s12985-017-0891-5. Virol J. 2017. PMID: 29132393 Free PMC article.
-
The BHLF1 Locus of Epstein-Barr Virus Contributes to Viral Latency and B-Cell Immortalization.J Virol. 2020 Aug 17;94(17):e01215-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01215-20. Print 2020 Aug 17. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 32581094 Free PMC article.
-
Unexpected patterns of Epstein-Barr virus transcription revealed by a high throughput PCR array for absolute quantification of viral mRNA.Virology. 2015 Jan 1;474:117-30. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2014.10.030. Epub 2014 Nov 15. Virology. 2015. PMID: 25463610 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr virus-encoded EBNA1 and ZEBRA: targets for therapeutic strategies against EBV-carrying cancers.J Pathol. 2015 Jan;235(2):334-41. doi: 10.1002/path.4431. J Pathol. 2015. PMID: 25186125 Review.
-
Human B cells on their route to latent infection--early but transient expression of lytic genes of Epstein-Barr virus.Eur J Cell Biol. 2012 Jan;91(1):65-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2011.01.014. Epub 2011 Mar 29. Eur J Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 21450364 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of ARKL1 as a Negative Regulator of Epstein-Barr Virus Reactivation.J Virol. 2019 Sep 30;93(20):e00989-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00989-19. Print 2019 Oct 15. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 31341047 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic Epstein-Barr virus gene expression on the path to B-cell transformation.Adv Virus Res. 2014;88:279-313. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-800098-4.00006-4. Adv Virus Res. 2014. PMID: 24373315 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive profiling of EBV gene expression in nasopharyngeal carcinoma through paired-end transcriptome sequencing.Front Med. 2016 Mar;10(1):61-75. doi: 10.1007/s11684-016-0436-0. Epub 2016 Mar 11. Front Med. 2016. PMID: 26969667
-
A Genome-Wide Epstein-Barr Virus Polyadenylation Map and Its Antisense RNA to EBNA.J Virol. 2019 Jan 4;93(2):e01593-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01593-18. Print 2019 Jan 15. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 30355690 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Virally Encoded Circular RNAs in the Pathogenicity of Human Oncogenic Viruses.Front Microbiol. 2021 Apr 20;12:657036. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.657036. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33959113 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Dolan, A., C. Addison, D. Gatherer, A. J. Davison, and D. J. McGeoch. 2006. The genome of Epstein-Barr virus type 2 strain AG876. Virology 350:164-170. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

