Assessing the effect of the CLPG mutation on the microRNA catalog of skeletal muscle using high-throughput sequencing
- PMID: 20944086
- PMCID: PMC2989991
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.108787.110
Assessing the effect of the CLPG mutation on the microRNA catalog of skeletal muscle using high-throughput sequencing
Abstract
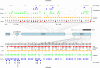
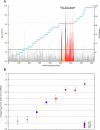
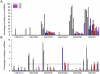
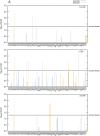
The callipyge phenotype is a monogenic muscular hypertrophy that is only expressed in heterozygous sheep receiving the CLPG mutation from their sire. The wild-type phenotype of CLPG/CLPG animals is thought to result from translational inhibition of paternally expressed DLK1 transcripts by maternally expressed miRNAs. To identify the miRNA responsible for this trans effect, we used high-throughput sequencing to exhaustively catalog miRNAs expressed in skeletal muscle of sheep of the four CLPG genotypes. We have identified 747 miRNA species of which 110 map to the DLK1-GTL2 or callipyge domain. We demonstrate that the latter are imprinted and preferentially expressed from the maternal allele. We show that the CLPG mutation affects their level of expression in cis (∼3.2-fold increase) as well as in trans (∼1.8-fold increase). In CLPG/CLPG animals, miRNAs from the DLK1-GTL2 domain account for ∼20% of miRNAs in skeletal muscle. We show that the CLPG genotype affects the levels of A-to-I editing of at least five pri-miRNAs of the DLK1-GTL2 domain, but that levels of editing of mature miRNAs are always minor. We present suggestive evidence that the miRNAs from the domain target the ORF of DLK1, thereby causing the trans inhibition underlying polar overdominance. We highlight the limitations of high-throughput sequencing for digital gene expression profiling as a result of biased and inconsistent amplification of specific miRNAs.
Figures


References
-
- Byrne K, Colgrave ML, Vuocolo T, Pearson R, Bidwell CA, Cockett NE, Lynn DJ, Fleming-Waddell JN, Tellam RL 2010. The imprinted retrotransposon-like gene PEG11 (RTL1) is expressed as a full-length protein in skeletal muscle from Callipyge sheep. PLoS ONE 5: e8638 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008638 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cavaille J, Seitz H, Paulsen M, Ferguson-Smith AC, Bachellerie JP 2002. Identification of tandemly-repeated C/D snoRNA genes at the imprinted human 14q32 domain reminiscent of those at the Prader-Willi/Angelman syndrome region. Hum Mol Genet 11: 1527–1538 - PubMed
-
- Charlier C, Segers K, Karim L, Shay T, Gyapay G, Cockett N, Georges M 2001a. The callipyge mutation enhances the expression of coregulated imprinted genes in cis without affecting their imprinting status. Nat Genet 27: 367–369 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
