Triple negativity and young age as prognostic factors in lymph node-negative invasive ductal carcinoma of 1 cm or less
- PMID: 20946688
- PMCID: PMC2966467
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-10-557
Triple negativity and young age as prognostic factors in lymph node-negative invasive ductal carcinoma of 1 cm or less
Abstract
Background: Whether a systemic adjuvant treatment is needed is an area of controversy in patients with node-negative early breast cancer with tumor size of ≤1 cm, including T1mic.
Methods: We performed a retrospective analysis of clinical and pathology data of all consecutive patients with node-negative T1mic, T1a, and T1b invasive ductal carcinoma who received surgery between Jan 2000 and Dec 2006. The recurrence free survival (RFS) and risk factors for recurrence were identified.
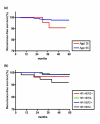
Results: Out of 3889 patients diagnosed with breast cancer, 375 patients were enrolled (T1mic:120, T1a:93, T1b:162). Median age at diagnosis was 49. After a median follow up of 60.8 months, 12 patients developed recurrences (T1mic:4 (3.3%), T1a:2 (2.2%), T1b:6 (3.7%)), with a five-year cumulative RFS rate of 97.2%. Distant recurrence was identified in three patients. Age younger than 35 years (HR 4.91; 95% CI 1.014-23.763, p = 0.048) and triple negative disease (HR 4.93; 95% CI 1.312-18.519, p = 0.018) were significantly associated with a higher rate of recurrence. HER2 overexpression, Ki-67, and p53 status did not affect RFS.
Conclusions: Prognosis of node-negative breast cancer with T1mic, T1a and T1b is excellent, but patients under 35 years of age or with triple negative disease have a relatively high risk of recurrence.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Distant invasive breast cancer recurrence risk in human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive T1a and T1b node-negative localized breast cancer diagnosed from 2000 to 2006: a cohort from an integrated health care delivery system.J Clin Oncol. 2014 Jul 10;32(20):2151-8. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2013.52.0858. Epub 2014 Jun 2. J Clin Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24888815
-
Risk factors for lymph node metastases in breast ductal carcinoma in situ with minimal invasive component.Arch Surg. 2002 Nov;137(11):1249-52. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.137.11.1249. Arch Surg. 2002. PMID: 12413311
-
Favorable prognosis in patients with T1a/T1bN0 triple-negative breast cancers treated with multimodality therapy.Cancer. 2012 Oct 15;118(20):4944-52. doi: 10.1002/cncr.27480. Epub 2012 Mar 5. Cancer. 2012. PMID: 22392492
-
Treatment of small (T1mic, T1a, and T1b) node-negative HER2+ breast cancer - a review of current evidence for and against the use of anti-HER2 treatment regimens.Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2022 May;22(5):505-522. doi: 10.1080/14737140.2022.2063844. Epub 2022 Apr 20. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2022. PMID: 35389302 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prognosis and management of patients with node-negative invasive breast carcinoma that is 1 cm or smaller in size (stage 1; T1a,bN0M0): a review of the literature.J Clin Oncol. 2006 May 1;24(13):2113-22. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2005.02.8035. J Clin Oncol. 2006. PMID: 16648513 Review.
Cited by
-
Characteristics and clinical outcome of pT1a-b node-negative breast cancer.North Clin Istanb. 2021 Mar 24;8(2):124-129. doi: 10.14744/nci.2020.06332. eCollection 2021. North Clin Istanb. 2021. PMID: 33851075 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Seven Gene Signature-Based Prognostic Model to Predict Distant Metastasis of Lymph Node-Negative Triple-Negative Breast Cancer.Front Oncol. 2021 Sep 16;11:746763. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.746763. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34604089 Free PMC article.
-
The Survival Outcomes of T1aN0M0 Triple-Negative Breast Cancer With Adjuvant Chemotherapy.Front Oncol. 2020 Sep 30;10:1753. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.01753. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33102205 Free PMC article.
-
Chemotherapy use and surgical treatment by receptor subtype in node-negative T1a and T1b female breast cancers, Iowa SEER Registry, 2010 to 2012.Clin Breast Cancer. 2015 Feb;15(1):e27-34. doi: 10.1016/j.clbc.2014.07.009. Epub 2014 Aug 18. Clin Breast Cancer. 2015. PMID: 25245424 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Subtype May Be More Associated With Prognosis and Chemotherapy Benefit Than Tumor Size in T1N0 Breast Cancer Patients: An Analysis of 2,168 Patients for Possible De-Escalation Treatment.Front Oncol. 2021 Feb 19;11:636266. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.636266. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33680973 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Otto SJ, Fracheboud J, Looman CW, Broeders MJ, Boer R, Hendriks JH, Verbeek AL, de Koning HJ. Initiation of population-based mammography screening in Dutch municipalities and effect on breast-cancer mortality: a systematic review. Lancet. 2003;361(9367):1411–1417. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(03)13132-7. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous