Learning and memory performances in adolescent users of alcohol and marijuana: interactive effects
- PMID: 20946746
- PMCID: PMC2965487
- DOI: 10.15288/jsad.2010.71.885
Learning and memory performances in adolescent users of alcohol and marijuana: interactive effects
Abstract
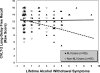
Objective: Lifetime alcohol hangover and withdrawal symptoms in youth have been shown to predict poorer recall of verbal and nonverbal information, as well as reduced visuospatial skills. Some evidence has suggested that negative effects of alcohol on the brain may be buffered in part by potential neuroprotective properties of cannabinoids. We hypothesized that a history of more alcohol hangover symptoms would predict worse performances on measures of verbal and visual memory, and that this relationship would be moderated by marijuana involvement.
Method: Participants were 130 adolescents (65 with histories of heavy marijuana use, and 65 non-marijuana-using controls), ranging in age from 15.7 to 19.1 years. Neuropsychological tests for visual and verbal memory and interviews assessing lifetime and recent substance use, hangover/withdrawal symptoms, and abuse and dependence criteria were administered.
Results: Regression models revealed that greater alcohol hangover symptoms predicted worse verbal learning (p < .05) and memory (p < .05) (California Verbal Learning Test, Second Edition) scores for non-marijuana users, but alcohol hangover symptoms were not linked to performance among marijuana users. Alcohol hangover symptoms did not predict visual memory in either group.
Conclusions: Results confirm previous studies linking adolescent heavy drinking to reduced verbal learning and memory performance. However, this relationship is not seen in adolescents with similar levels of alcohol involvement who also are heavy users of marijuana.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Heavy alcohol use, marijuana use, and concomitant use by adolescents are associated with unique and shared cognitive decrements.J Int Neuropsychol Soc. 2014 Sep;20(8):784-95. doi: 10.1017/S1355617714000666. J Int Neuropsychol Soc. 2014. PMID: 25241623 Free PMC article.
-
Adolescent substance abuse: the effects of alcohol and marijuana on neuropsychological performance.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2011 Jan;35(1):39-46. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2010.01320.x. Epub 2010 Oct 19. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2011. PMID: 20958330 Free PMC article.
-
Longitudinal study of cognition among adolescent marijuana users over three weeks of abstinence.Addict Behav. 2010 Nov;35(11):970-6. doi: 10.1016/j.addbeh.2010.06.012. Epub 2010 Jun 13. Addict Behav. 2010. PMID: 20621421 Free PMC article.
-
The influence of marijuana use on neurocognitive functioning in adolescents.Curr Drug Abuse Rev. 2008 Jan;1(1):99-111. doi: 10.2174/1874473710801010099. Curr Drug Abuse Rev. 2008. PMID: 19630709 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Drug-related decrease in neuropsychological functions of abstinent drug users.Curr Drug Abuse Rev. 2011 Mar;4(1):42-56. doi: 10.2174/1874473711104010042. Curr Drug Abuse Rev. 2011. PMID: 21466500 Review.
Cited by
-
Neuropsychological performance in adolescent marijuana users with co-occurring alcohol use: A three-year longitudinal study.Neuropsychology. 2015 Nov;29(6):829-843. doi: 10.1037/neu0000203. Epub 2015 May 4. Neuropsychology. 2015. PMID: 25938918 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of alcohol use on human adolescent brain structures and systems.Handb Clin Neurol. 2014;125:501-10. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-444-62619-6.00028-8. Handb Clin Neurol. 2014. PMID: 25307592 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Primed for addiction: A critical review of the role of microglia in the neurodevelopmental consequences of adolescent alcohol drinking.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2021 Oct;45(10):1908-1926. doi: 10.1111/acer.14694. Epub 2021 Sep 5. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2021. PMID: 34486128 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cognitive functioning of adolescent and young adult cannabis users in the Philadelphia Neurodevelopmental Cohort.Psychol Addict Behav. 2017 Jun;31(4):423-434. doi: 10.1037/adb0000268. Epub 2017 Apr 17. Psychol Addict Behav. 2017. PMID: 28414475 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of alcohol use on neuroimaging correlates of cognitive and emotional processing in human adolescence.Neuropsychology. 2019 Sep;33(6):781-794. doi: 10.1037/neu0000555. Neuropsychology. 2019. PMID: 31448946 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aiken LS, West SG, Reno RR. Multiple regression: Testing and interpreting interactions. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage; 1991.
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. 4th ed. Washington, DC: Author; 1994.
-
- Bates ME, Bowden SC, Barry D. Neurocognitive impairment associated with alcohol use disorders: Implications for treatment. Experimental and Clinical Psychopharmacology. 2002;10:193–212. - PubMed
-
- Beck AT, Ward CH, Mendelson M, Mock J, Erbaugh J. An inventory for measuring depression. Archives of General Psychiatry. 1961;4:561–571. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

