Structural analysis of RNA in living cells by in vivo synchrotron X-ray footprinting
- PMID: 20946773
- PMCID: PMC3144761
- DOI: 10.1016/S0076-6879(09)68012-5
Structural analysis of RNA in living cells by in vivo synchrotron X-ray footprinting
Abstract
Chemical footprinting methods are widely used to probe the solution structures of nucleic acids and their complexes. Among the many available modifying reagents, hydroxyl radical is exceptional in its ability to provide nucleotide-level information on the solvent accessibility of the nucleic acid backbone. Until recently, hydroxyl radical footprinting has been limited to in vitro experiments. We describe the use of synchrotron X-radiation to generate hydroxyl radicals within cells for effective footprinting of RNA-protein complexes in vivo. This technique gives results that are consistent with in vitro footprinting experiments, with differences reflecting apparent structural changes to the RNA in vivo.
Copyright © 2009 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
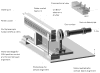
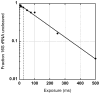
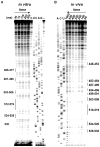

References
-
- Balzer M, Wagner R. A chemical modification method for the structural analysis of RNA and RNA-protein complexes within living cells. Anal Biochem. 1998;256(2):240–242. - PubMed
-
- Burkhoff AM, Tullius TD. The unusual conformation adopted by the adenine tracts in kinetoplast DNA. Cell. 1987;48(6):935–943. - PubMed
-
- Cadet J, Bellon S, Douki T, Frelon S, Gasparutto D, Muller E, Pouget JP, Ravanat JL, Romieu A, Sauvaigo S. Radiation-induced DNA damage: formation, measurement, and biochemical features. J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol. 2004;23(1):33–43. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

