Use of deoxyribozymes in RNA research
- PMID: 20946786
- PMCID: PMC2957665
- DOI: 10.1016/S0076-6879(09)69005-4
Use of deoxyribozymes in RNA research
Abstract
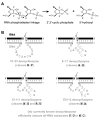
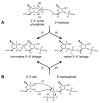
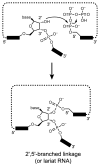
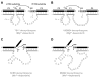
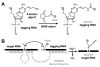
Since their first identification by in vitro selection in 1994, deoxyribozymes have been developed to catalyze a variety of chemical reactions. The first DNA-catalyzed reaction was cleavage of a ribonucleotide linkage within an oligonucleotide substrate. In subsequent years, growing collections of deoxyribozymes have been developed for several reactions that have practical utility for RNA research. These deoxyribozymes are useful for site-specific RNA cleavage as well as ligation to form linear, branched, and lariat RNA products. An application related to RNA ligation is deoxyribozyme-catalyzed labeling of RNA (DECAL), which is used to attach a biophysical tag to a desired RNA sequence at a specific position. With current achievements and likely future developments, deoxyribozymes are a useful contributor to the toolbox of RNA research methods.
Copyright © 2009 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
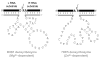
Similar articles
-
New Deoxyribozymes for the Native Ligation of RNA.Molecules. 2020 Aug 11;25(16):3650. doi: 10.3390/molecules25163650. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32796587 Free PMC article.
-
Deoxyribozymes: useful DNA catalysts in vitro and in vivo.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2008 Jul;65(14):2156-74. doi: 10.1007/s00018-008-8029-y. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2008. PMID: 18373062 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rational modification of a selection strategy leads to deoxyribozymes that create native 3'-5' RNA linkages.J Am Chem Soc. 2004 Dec 22;126(50):16426-32. doi: 10.1021/ja045817x. J Am Chem Soc. 2004. PMID: 15600344
-
Zn2+-dependent deoxyribozymes that form natural and unnatural RNA linkages.Biochemistry. 2005 Jun 28;44(25):9217-31. doi: 10.1021/bi050146g. Biochemistry. 2005. PMID: 15966746 Free PMC article.
-
Deoxyribozymes: DNA catalysts for bioorganic chemistry.Org Biomol Chem. 2004 Oct 7;2(19):2701-6. doi: 10.1039/B411910J. Epub 2004 Sep 3. Org Biomol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15455136 Review.
Cited by
-
Establishing broad generality of DNA catalysts for site-specific hydrolysis of single-stranded DNA.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Feb;40(4):1778-86. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr860. Epub 2011 Oct 22. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22021383 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic Contacts of U2, RES, Cwc25, Prp8 and Prp45 Proteins with the Pre-mRNA Branch-Site and 3' Splice Site during Catalytic Activation and Step 1 Catalysis in Yeast Spliceosomes.PLoS Genet. 2015 Sep 22;11(9):e1005539. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005539. eCollection 2015. PLoS Genet. 2015. PMID: 26393790 Free PMC article.
-
DNA as a versatile chemical component for catalysis, encoding, and stereocontrol.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2010 Sep 24;49(40):7180-201. doi: 10.1002/anie.200906345. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2010. PMID: 20669202 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Site-Selective RNA Splicing Nanozyme: DNAzyme and RtcB Conjugates on a Gold Nanoparticle.ACS Chem Biol. 2018 Jan 19;13(1):215-224. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.7b00437. Epub 2017 Dec 19. ACS Chem Biol. 2018. PMID: 29155548 Free PMC article.
-
DNA Oligonucleotide 3'-Phosphorylation by a DNA Enzyme.Biochemistry. 2016 May 10;55(18):2671-6. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.6b00151. Epub 2016 Apr 26. Biochemistry. 2016. PMID: 27063020 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

