Making temperature-sensitive mutants
- PMID: 20946811
- PMCID: PMC2957654
- DOI: 10.1016/S0076-6879(10)70008-2
Making temperature-sensitive mutants
Abstract
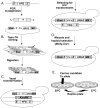
The study of temperature-sensitive (Ts) mutant phenotypes is fundamental to gene identification and for dissecting essential gene function. In this chapter, we describe two "shuffling" methods for producing Ts mutants using a combination of PCR, in vivo recombination, and transformation of diploid strains heterozygous for a knockout of the desired mutation. The main difference between the two methods is the type of strain produced. In the "plasmid" version, the product is a knockout mutant carrying a centromeric plasmid carrying the Ts mutant. In the "chromosomal" version, The Ts alleles are integrated directly into the endogenous locus, albeit not in an entirely native configuration. Both variations have their strengths and weaknesses, which are discussed here.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Brachmann CB, et al. Designer deletion strains derived from Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C: a useful set of strains and plasmids for PCR-mediated gene disruption and other applications. Yeast. 1998;14:115–32. - PubMed
-
- Gietz RD, et al. Studies on the transformation of intact yeast cells by the LiAc/SS-DNA/PEG procedure. Yeast. 1995;11:355–60. - PubMed
-
- Gietz RD, Sugino A. New yeast-Escherichia coli shuttle vectors constructed with in vitro mutagenized yeast genes lacking six-base pair restriction sites. Gene. 1988;74:527–34. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

