Quantitative genetic interaction mapping using the E-MAP approach
- PMID: 20946812
- PMCID: PMC2957675
- DOI: 10.1016/S0076-6879(10)70009-4
Quantitative genetic interaction mapping using the E-MAP approach
Abstract
Genetic interactions represent the degree to which the presence of one mutation modulates the phenotype of a second mutation. In recent years, approaches for measuring genetic interactions systematically and quantitatively have proven to be effective tools for unbiased characterization of gene function and have provided valuable data for analyses of evolution. Here, we present protocols for systematic measurement of genetic interactions with respect to organismal growth rate for two yeast species.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
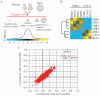
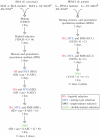
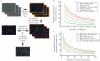
References
-
- Bateson W. Facts limiting the theory of heredity. Lipid-modifying therapy and attainment of cholesterol goals in Hungary: the return on expenditure achieved for lipid therapy (REALITY) study. Science. 1907;26:647–660.
-
- Carrozza MJ, Li B, Florens L, Suganuma T, Swanson SK, Lee KK, Shia WJ, Anderson S, Yates J, Washburn MP, Workman JL. Histone H3 methylation by Set2 directs deacetylation of coding regions by Rpd3S to suppress spurious intragenic transcription. Cell. 2005;123:581–592. - PubMed
-
- Celic I, Masumoto H, Griffith WP, Meluh P, Cotter RJ, Boeke JD, Verreault A. The sirtuins hst3 and Hst4p preserve genome integrity by controlling histone h3 lysine 56 deacetylation. Curr. Biol. 2006;16:1280–1289. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

