Degree of modification of Ro60 by the lipid peroxidation by-product 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal may differentially induce Sjögren syndrome or systemic lupus erythematosus in BALB/c mice
- PMID: 20946951
- PMCID: PMC3591494
- DOI: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2010.10.687
Degree of modification of Ro60 by the lipid peroxidation by-product 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal may differentially induce Sjögren syndrome or systemic lupus erythematosus in BALB/c mice
Abstract
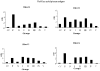
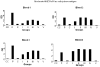
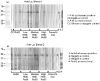
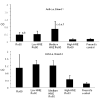
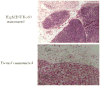
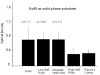
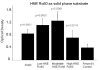
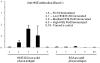
Our previous work showed that immunization of rabbits with 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal-modified Ro60 (HNE-Ro60) accelerates autoimmunity. We extended this model into mice, hypothesizing that the severity of autoimmunity would be dependent on the degree of HNE modification of Ro60. Five groups of BALB/c mice (10/group) were used. Group I was immunized with Ro60. Groups II to IV were immunized with Ro60 modified with 0.4 mM (low), 2 mM (medium), and 10 mM (high) HNE, respectively. Group V controls received Freund's adjuvant. A rapid abrogation of tolerance to Ro60/La antigens occurred in mice immunized with HNE-modified Ro60, especially in the low and medium HNE-Ro60 groups. Lymphocytic infiltration and significantly high decrement in salivary flow (37%) compared to controls was observed only in the high HNE-Ro60 group, suggesting induction of a Sjögren syndrome-like condition in this group. Anti-dsDNA occurred only in mice immunized with medium HNE-Ro60. This group did not have a significant decrement in salivary flow, suggesting induction of a systemic lupus erythematosus-like manifestation in this group. Significantly high antibodies to Ro60 were found in saliva of mice in the low and medium HNE-Ro60 and the Ro60 groups, as well as anti-HNE Ro60 in the low and medium HNE-Ro60 groups. Understanding the mechanism of this differential induction may help discriminate between these two autoimmune diseases.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Experimental induction of anti-muscarinic type-3-receptor extracellular loop antibodies by immunization with 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal modified Ro60 and unmodified Ro60.Clin Exp Immunol. 2025 Jan 21;219(1):uxae114. doi: 10.1093/cei/uxae114. Clin Exp Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39658078
-
Location of immunization and interferon-γ are central to induction of salivary gland dysfunction in Ro60 peptide immunized model of Sjögren's syndrome.PLoS One. 2011 Mar 28;6(3):e18003. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0018003. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21464925 Free PMC article.
-
Immunization with 60 kD Ro peptide produces different stages of preclinical autoimmunity in a Sjögren's syndrome model among multiple strains of inbred mice.Clin Exp Immunol. 2013 Jul;173(1):67-75. doi: 10.1111/cei.12094. Clin Exp Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23607771 Free PMC article.
-
A review of the role and clinical utility of anti-Ro52/TRIM21 in systemic autoimmunity.Rheumatol Int. 2017 Aug;37(8):1323-1333. doi: 10.1007/s00296-017-3718-1. Epub 2017 Apr 17. Rheumatol Int. 2017. PMID: 28417151 Review.
-
Sjögren syndrome and systemic lupus erythematosus are distinct conditions.Dermatol Online J. 2006 Jan 27;12(1):4. Dermatol Online J. 2006. PMID: 16638372 Review.
Cited by
-
Significance of Lipid-Derived Reactive Aldehyde-Specific Immune Complexes in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.PLoS One. 2016 Oct 17;11(10):e0164739. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0164739. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27749917 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative stress as a potential causal factor for autoimmune hemolytic anemia and systemic lupus erythematosus.World J Nephrol. 2015 May 6;4(2):213-22. doi: 10.5527/wjn.v4.i2.213. World J Nephrol. 2015. PMID: 25949934 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase (G6PD) Deficiency and Long-Term Risk of Immune-Related diseases.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Mar 24:2023.03.23.23287616. doi: 10.1101/2023.03.23.23287616. medRxiv. 2023. Update in: Front Immunol. 2023 Sep 11;14:1232560. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1232560. PMID: 37090544 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Ro60-Roles in RNA Processing, Inflammation, and Rheumatic Autoimmune Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 14;25(14):7705. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147705. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39062948 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oxidative post-translational modifications and their involvement in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases.Redox Biol. 2014 May 28;2:715-24. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2014.05.004. eCollection 2014. Redox Biol. 2014. PMID: 24955328 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Scofield RH, Asfa S, Obeso D, Jonsson R, Kurien BT. Immunization with short peptides from the 60-kDa Ro antigen recapitulates the serological and pathological findings as well as the salivary gland dysfunction of Sjogren's syndrome. J Immunol. 2005;175:8409–14. - PubMed
-
- Mathews SA, Kurien BT, Scofield RH. Oral manifestations of Sjögren's syndrome. J Dent Res. 2008;87:308–18. - PubMed
-
- Farris AD, Gross JK, Hanas JS, Harley JB. Genes for murine Y1 and Y3 Ro RNAs have class 3 RNA polymerase III promoter structures and are unlinked on mouse chromosome 6. Gene. 1996;174:35–42. - PubMed
-
- O'Brien CA, Wolin SL. A possible role for the 60-kDa Ro autoantigen in a discard pathway for defective 5S rRNA precursors. Genes Dev. 1994;8:2891–903. - PubMed
-
- Scofield RH, Kurien BT, Zhang F, Mehta P, Kaufman K, Gross T, Bachmann M, Gordon T, Harley JB. Protein-protein interaction of the Ro-ribonucleoprotein particle using multiple antigenic peptides. Mol Immunol. 1999;36:1093–106. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

