p38α MAPK is a MTOC-associated protein regulating spindle assembly, spindle length and accurate chromosome segregation during mouse oocyte meiotic maturation
- PMID: 20948319
- PMCID: PMC3055197
- DOI: 10.4161/cc.9.20.13389
p38α MAPK is a MTOC-associated protein regulating spindle assembly, spindle length and accurate chromosome segregation during mouse oocyte meiotic maturation
Abstract
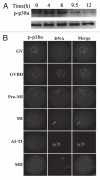
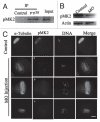
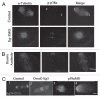
P38αMAPK (p38α) is usually activated in response to various stresses and plays a role in the inhibition of cell proliferation and tumor progression, but little is known about its roles in meiotic spindle assembly. In this study, we characterized the dynamic localization of p38α and explored its function in mouse oocyte meiotic maturation. P38α specifically colocalized with γ-tubulin and Plk1 at the center of MTOCs and spindle poles. Depletion of p38α by specific morpholino injection resulted in severely defective spindles and misaligned chromosomes probably via MK2 dephosphorylation. Notably, depletion of p38α led to significant spindle pole defects, spindle elongation, non-tethered kinetochore microtubules and increased microtubule tension. The disruption of spindle stability was coupled with decreased γ-tubulin and Plk1 at MTOCs. Overexpression of Eg5, a conserved motor protein, also caused spindle elongation and its morpholino injection almost completely rescued spindle elongation caused by p38α depletion. In addition, p38α-depletion decreased BubR1 and interfered with spindle assembly checkpoint (SAC), which resulted in aneuploid oocytes. Together, these data indicate that p38α is an important component of MTOCs, which regulates spindle assembly and spindle length, as well as stabilizes the spindle and spindle poles. Perturbed SAC and abnormal microtubule tension may be responsible for the misaligned chromosomes and high aneuploidy in p38α-depleted mouse oocytes.
Figures






Similar articles
-
CIP2A acts as a scaffold for CEP192-mediated microtubule organizing center assembly by recruiting Plk1 and aurora A during meiotic maturation.Development. 2017 Oct 15;144(20):3829-3839. doi: 10.1242/dev.158584. Epub 2017 Sep 21. Development. 2017. PMID: 28935709
-
Unique subcellular distribution of phosphorylated Plk1 (Ser137 and Thr210) in mouse oocytes during meiotic division and pPlk1(Ser137) involvement in spindle formation and REC8 cleavage.Cell Cycle. 2015;14(22):3566-79. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2015.1100770. Cell Cycle. 2015. PMID: 26654596 Free PMC article.
-
NEDD1 is crucial for meiotic spindle stability and accurate chromosome segregation in mammalian oocytes.Dev Biol. 2010 Mar 15;339(2):439-50. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2010.01.009. Epub 2010 Jan 15. Dev Biol. 2010. PMID: 20079731
-
[Kinesin-14 leaps to pole position in bipolar spindle assembly].Ai Zheng. 2008 Sep;27(9):989-92. Ai Zheng. 2008. PMID: 18799042 Review. Chinese.
-
Oocyte Meiotic Spindle Assembly and Function.Curr Top Dev Biol. 2016;116:65-98. doi: 10.1016/bs.ctdb.2015.11.031. Epub 2016 Jan 23. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2016. PMID: 26970614 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Azoxystrobin exposure impairs meiotic maturation by disturbing spindle formation in mouse oocytes.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Dec 2;10:1053654. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.1053654. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 36531942 Free PMC article.
-
Nicotinamide boosts oocyte quantity and quality by promoting N4-acetylation modification in lupus mice.Sci Adv. 2025 Jul 18;11(29):eadu0955. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adu0955. Epub 2025 Jul 18. Sci Adv. 2025. PMID: 40680131 Free PMC article.
-
Nek9 regulates spindle organization and cell cycle progression during mouse oocyte meiosis and its location in early embryo mitosis.Cell Cycle. 2012 Dec 1;11(23):4366-77. doi: 10.4161/cc.22690. Epub 2012 Nov 16. Cell Cycle. 2012. PMID: 23159858 Free PMC article.
-
Kif2a regulates spindle organization and cell cycle progression in meiotic oocytes.Sci Rep. 2016 Dec 19;6:38574. doi: 10.1038/srep38574. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27991495 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative Stress Induces Mouse Follicular Granulosa Cells Apoptosis via JNK/FoxO1 Pathway.PLoS One. 2016 Dec 9;11(12):e0167869. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0167869. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27936150 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Compton DA. Spindle assembly in animal cells. Annu Rev Biochem. 2000;69:95–114. - PubMed
-
- Taylor SS, Scott MI, Holland AJ. The spindle checkpoint: a quality control mechanism which ensures accurate chromosome segregation. Chromosome Res. 2004;12:599–616. - PubMed
-
- Kastan MB, Bartek J. Cell cycle checkpoints and cancer. Nature. 2004;432:316–323. - PubMed
-
- Martin RH. Meiotic errors in human oogenesis and spermatogenesis. Reprod Biomed Online. 2008;16:523–531. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
