Adoptive transfer of EBV-specific T cells results in sustained clinical responses in patients with locoregional nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- PMID: 20948438
- PMCID: PMC2964409
- DOI: 10.1097/CJI.0b013e3181f3cbf4
Adoptive transfer of EBV-specific T cells results in sustained clinical responses in patients with locoregional nasopharyngeal carcinoma
Abstract
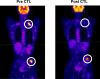
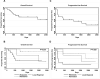
Patients with recurrent or refractory Epstein Barr Virus (EBV)-positive nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) continue to have poor outcomes. Our earlier Phase I dose escalation clinical study of 10 NPC patients showed that infusion of EBV-specific cytotoxic T cells (EBV-CTLs) was safe and had antitumor activity. To better define the overall response rate and discover whether disease status, EBV-antigen specificity, and/or in vivo expansion of infused EBV-CTLs predicted outcome, we treated 13 additional NPC patients with EBV-CTLs in a fixed-dose, Phase II component of the study. We assessed toxicity, efficacy, specificity, and expansion of infused CTLs for all 23 recurrent/refractory NPC patients treated on this Phase I/II clinical study. At the time of CTL infusion, 8 relapsed NPC patients were in remission and 15 had active disease. No significant toxicity was observed. Of the relapsed patients treated in their second or subsequent remission, 62% (5/8) remain disease free (at 17 to 75 mo), whereas 48.7% (7/15) of those with active disease had a CR/CRu (33.3%) or PR (15.4%). In contrast to locoregional disease, metastatic disease was associated with an increased risk of disease progression (HR: 3.91, P=0.015) and decreased overall survival (HR: 5.55, P=0.022). Neither the specificity of the infused CTLs for particular EBV antigens nor their measurable in vivo expansion discernibly influenced outcome. In conclusion, treatment of patients with relapsed/refractory EBV-positive NPC with EBV-CTLs is safe and can be associated with significant, long-term clinical benefit, particularly for patients with locoregional disease.
Figures

References
-
- Chan AT, Teo PM, Johnson PJ. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Ann Oncol. 2002;13:1007–15. - PubMed
-
- Raab-Traub N. Epstein-Barr virus in the pathogenesis of NPC. Semin Cancer Biol. 2002;12:431–41. - PubMed
-
- Mould RF, Tai TH. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma: treatments and outcomes in the 20th century. Br J Radiol. 2002;75:307–39. - PubMed
-
- Ayan I, Kaytan E, Ayan N. Childhood nasopharyngeal carcinoma: from biology to treatment. Lancet Oncol. 2003;4:13–21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

