Traf7, a MyoD1 transcriptional target, regulates nuclear factor-κB activity during myogenesis
- PMID: 20948544
- PMCID: PMC2999857
- DOI: 10.1038/embor.2010.154
Traf7, a MyoD1 transcriptional target, regulates nuclear factor-κB activity during myogenesis
Abstract
We have identified the E3 ligase Traf7 as a direct MyoD1 target and show that cell cycle exit-an early event in muscle differentiation-is linked to decreased Traf7 expression. Depletion of Traf7 accelerates myogenesis, in part through downregulation of nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) activity. We used a proteomic screen to identify NEMO, the NF-κB essential modulator, as a Traf7-interacting protein. Finally, we show that ubiquitylation of NF-κB essential modulator is regulated exclusively by Traf7 activity in myoblasts. Our results suggest a new mechanism by which MyoD1 function is coupled to NF-κB activity through Traf7, regulating the balance between cell cycle progression and differentiation during myogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
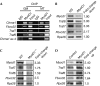

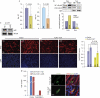
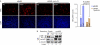

References
-
- Ha H, Han D, Choi Y (2009) Traf-mediated TNFR-family signaling. Curr Protoc Immunol Ch. 11, Unit 11.9D - PubMed
-
- Halevy O, Novitch BG, Spicer DB, Skapek SX, Rhee J, Hannon GJ, Beach D, Lassar AB (1995) Correlation of terminal cell cycle arrest of skeletal muscle with induction of p21 by MyoD. Science 267: 1018–1021 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

