Structural transformation of the tandem ubiquitin-interacting motifs in ataxin-3 and their cooperative interactions with ubiquitin chains
- PMID: 20949063
- PMCID: PMC2951365
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0013202
Structural transformation of the tandem ubiquitin-interacting motifs in ataxin-3 and their cooperative interactions with ubiquitin chains
Abstract
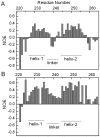
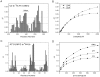
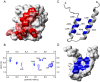
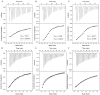
The ubiquitin-interacting motif (UIM) is a short peptide with dual function of binding ubiquitin (Ub) and promoting ubiquitination. We elucidated the structures and dynamics of the tandem UIMs of ataxin-3 (AT3-UIM12) both in free and Ub-bound forms. The solution structure of free AT3-UIM12 consists of two α-helices and a flexible linker, whereas that of the Ub-bound form is much more compact with hydrophobic contacts between the two helices. NMR dynamics indicates that the flexible linker becomes rigid when AT3-UIM12 binds with Ub. Isothermal titration calorimetry and NMR titration demonstrate that AT3-UIM12 binds diUb with two distinct affinities, and the linker plays a critical role in association of the two helices in diUb binding. These results provide an implication that the tandem UIM12 interacts with Ub or diUb in a cooperative manner through an allosteric effect and dynamics change of the linker region, which might be related to its recognitions with various Ub chains and ubiquitinated substrates.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Hofmann K, Falquet L. A ubiquitin-interacting motif conserved in components of the proteasomal and lysosomal protein degradation systems. Trends Biochem Sci. 2001;26:347–350. - PubMed
-
- Miller SL, Malotky E, O'Bryan JP. Analysis of the role of ubiquitin-interacting motifs in ubiquitin binding and ubiquitylation. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:33528–33537. - PubMed
-
- Young P, Deveraux Q, Beal RE, Pickart CM, Rechsteiner M. Characterization of two polyubiquitin binding sites in the 26 S protease subunit 5a. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:5461–5467. - PubMed
-
- Oldham CE, Mohney RP, Miller SL, Hanes RN, O'Bryan JP. The ubiquitin-interacting motifs target the endocytic adaptor protein epsin for ubiquitination. Curr Biol. 2002;12:1112–1116. - PubMed
-
- Polo S, Sigismund S, Faretta M, Guidi M, Capua MR, et al. A single motif responsible for ubiquitin recognition and monoubiquitination in endocytic proteins. Nature. 2002;416:451–455. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

