Self-protecting bactericidal titanium alloy surface formed by covalent bonding of daptomycin bisphosphonates
- PMID: 20949909
- PMCID: PMC2987735
- DOI: 10.1021/bc100136e
Self-protecting bactericidal titanium alloy surface formed by covalent bonding of daptomycin bisphosphonates
Abstract
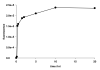
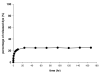
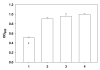
Infections are a devastating complication of titanium alloy orthopedic implants. Current therapy includes antibiotic-impregnated bone cement and antibiotic-containing coatings. We hypothesized that daptomycin, a Gram-positive peptide antibiotic, could prevent bacterial colonization on titanium alloy surfaces if covalently bonded via a flexible, hydrophilic spacer. We designed and synthesized a series of daptomycin conjugates for bonding to the surface of 1.0 cm² Ti6Al4V foils through bisphosphonate groups, reaching a maximum yield of 180 pmol/cm². Daptomycin-bonded foils killed 53 ± 5% of a high challenge dose of 3 × 10⁵ cfu Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 29213.
Figures





References
-
- Moss AJ, Hamburger S, Moore RM, Jr., Jeng LL, Howie LJ. Use of selected medical device implants in the United States, 1988. Adv Data. 1991:1–24. - PubMed
-
- Garvin KL, Hanssen AD. Infection after total hip arthroplasty: Past, present, and future. J. Bone Joint Surg. 1995;77A:1576–1588. - PubMed
-
- Mahan J, Seligson D, Henry SL, Hynes P, Dobbins J. Factors in pin tract infections. Orthopedics. 1991;14:305–308. - PubMed
-
- Duggan JM, Georgiadis GM, Kleshinski JF. Management of prosthetic joint infections. Infect. Med. 2001;18:534–541.
-
- Zimmerli W, Trampuz A, Ochsner PE. Prosthetic-joint infections. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:1645–54. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

