The ISG56/IFIT1 gene family
- PMID: 20950130
- PMCID: PMC3021354
- DOI: 10.1089/jir.2010.0101
The ISG56/IFIT1 gene family
Abstract
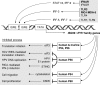
The ISG56/IFIT1 family of genes is clustered on human chromosome 10 and is comprised of 4 members, ISG56/IFIT1, ISG54/IFIT2, ISG60/IFIT3, and ISG58/IFIT5, whose homologs are evolutionarily conserved from mammals to amphibians. While these genes are normally silent in most cell types, their transcription is strongly induced by interferons, virus infection, and molecular patterns such as double-stranded RNA or lipopolysaccharides. The encoded P56 family proteins are characterized by multiple repeats of tetratricopeptide repeat helix-turn-helix motifs mediating a variety of protein-protein interactions, which result in a multitude of effects on cellular and viral functions, such as translation initiation, virus replication, double-stranded RNA signaling, cell migration, and proliferation.
Figures


References
-
- Bandyopadhyay SK. Leonard GT., Jr. Bandyopadhyay T. Stark GR. Sen GC. Transcriptional induction by double-stranded RNA is mediated by interferon-stimulated response elements without activation of interferon-stimulated gene factor 3. J Biol Chem. 1995;270(33):19624–19629. - PubMed
-
- Barnes BJ. Richards J. Mancl M. Hanash S. Beretta L. Pitha PM. Global and distinct targets of IRF-5 and IRF-7 during innate response to viral infection. J Biol Chem. 2004;279(43):45194–45207. - PubMed
-
- Bluyssen HA. Vlietstra RJ. Faber PW. Smit EM. Hagemeijer A. Trapman J. Structure, chromosome localization, and regulation of expression of the interferon-regulated mouse Ifi54/Ifi56 gene family. Genomics. 1994;24(1):137–148. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

