The global pediatric antiretroviral market: analyses of product availability and utilization reveal challenges for development of pediatric formulations and HIV/AIDS treatment in children
- PMID: 20950492
- PMCID: PMC2964660
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2431-10-74
The global pediatric antiretroviral market: analyses of product availability and utilization reveal challenges for development of pediatric formulations and HIV/AIDS treatment in children
Abstract
Background: Important advances in the development and production of quality-certified pediatric antiretroviral (ARV) formulations have recently been made despite significant market disincentives for manufacturers. This progress resulted from lobbying and innovative interventions from HIV/AIDS activists, civil society organizations, and international organizations. Research on uptake and dispersion of these improved products across countries and international organizations has not been conducted but is needed to inform next steps towards improving child health.
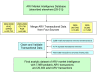
Methods: We used information from the World Health Organization Prequalification Programme and the United States Food and Drug Administration to describe trends in quality-certification of pediatric formulations and used 7,989 donor-funded, pediatric ARV purchase transactions from 2002-2009 to measure uptake and dispersion of new pediatric ARV formulations across countries and programs. Prices for new pediatric ARV formulations were compared to alternative dosage forms.
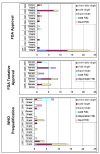
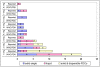
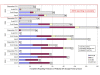
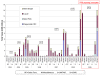
Results: Fewer ARV options exist for HIV/AIDS treatment in children than adults. Before 2005, most pediatric ARVs were produced by innovator companies in single-component solid and liquid forms. Five 2-in1 and four 3-in-1 generic pediatric fixed-dose combinations (FDCs) in solid and dispersible forms have been quality-certified since 2005. Most (67%) of these were produced by one quality-certified manufacturer. Uptake of new pediatric FDCs outside of UNITAID is low. UNITAID accounted for 97-100% of 2008-2009 market volume. In total, 33 and 34 countries reported solid or dispersible FDC purchases in 2008 and 2009, respectively, but most purchases were made through UNITAID. Only three Global Fund country recipients reported purchase of these FDCs in 2008. Prices for pediatric FDCs were considerably lower than liquids but typically higher than half of an adult FDC.
Conclusion: Pediatric ARV markets are more fragile than adult markets. Ensuring a long-term supply of quality, well-adapted ARVs for children requires ongoing monitoring and improved understanding of global pediatric markets, including country-based research to explain and address low uptake of new, improved formulations. Continued innovation in pediatric ARV development may be threatened by outdated procurement practices failing to connect clinicians making prescribing decisions, supply chain staff dealing with logistics, donors, international organizations, and pharmaceutical manufacturers. Perceptions of global demand must be better informed by accurate estimates of actual country-level demand.
Figures

References
-
- Dionisio D, Gass R, McDermott P, Racalbuto V, Madeo M, Braghieri G, Crowley S, Pinheiro EDS, Graaff P, Vasan A. et al.What Strategies to Boost Production of Affordable Fixed-Dose Anti-Retroviral Drug Combinations for Children in the Developing World? Current HIV Research. 2007;5(2):155–187. doi: 10.2174/157016207780077075. - DOI - PubMed
-
- UNAIDS, UNICEF. A call to action. Children: the missing face of AIDS. 2005.
-
- World Health Organization UNAIDS, UNICEF. Towards universal access: Scaling up priority HIV/AIDS interventions in the health sector. Progress report 2009. Geneva; 2009.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

