A role for flexible loops in enzyme catalysis
- PMID: 20951028
- PMCID: PMC2994964
- DOI: 10.1016/j.sbi.2010.09.005
A role for flexible loops in enzyme catalysis
Abstract
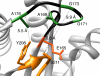
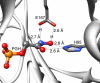
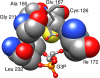
Triosephosphate isomerase (TIM), glycerol 3-phosphate dehydrogenase, and orotidine 5'-monophosphate decarboxylase each use the binding energy from the interaction of phosphite dianion with a flexible phosphate gripper loop to activate a second, phosphodianion-truncated, substrate towards enzyme-catalyzed proton transfer, hydride transfer, and decarboxylation, respectively. Studies on TIM suggest that the most important general effect of loop closure over the substrate phosphodianion, and the associated conformational changes, is to extrude water from the enzyme active site. This should cause a decrease in the effective active-site dielectric constant, and an increase in transition state stabilization from enhanced electrostatic interactions with polar amino acid side chains. The most important specific effect of these conformational changes is to increase the basicity of the carboxylate side chain of the active site glutamate base by its placement in a 'hydrophobic cage'.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
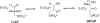
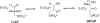
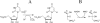


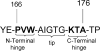




References
-
- Herschlag D. The role of induced fit and conformational changes of enzymes in specificity and catalysis. Biorg Chem. 1988;16:62–96.
-
- Jencks WP. Binding energy, specificity, and enzymic catalysis: the Circe effect. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1975;43:219–410. - PubMed
-
- Knowles JR. To build an enzyme. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. London, Ser. B. 1991;332:115–121. [An excellent summary of our understanding in 1991 of the challenges faced by TIM in catalyzing deprotonation of weakly acidic carbon, and of the chemical strategies adopted by this enzyme] - PubMed
-
- Raines RT, Sutton EL, Straus DR, Gilbert W, Knowles JR. Reaction energetics of a mutant triose phosphate isomerase in which the active-site glutamate has been changed to aspartate. Biochemistry. 1986;25:7142–7154. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

