SIV infection in natural hosts: resolution of immune activation during the acute-to-chronic transition phase
- PMID: 20951225
- PMCID: PMC3022004
- DOI: 10.1016/j.micinf.2010.09.011
SIV infection in natural hosts: resolution of immune activation during the acute-to-chronic transition phase
Abstract
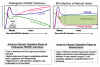
SIV-infected natural hosts do not progress to clinical AIDS yet display high viral replication and an acute immunologic response similar to pathogenic SIV/HIV infections. During chronic SIV infection, natural hosts suppress their immune activation, whereas pathogenic hosts display a highly activated immune state. Here, we review natural host SIV infections with an emphasis on specific immune cells and their contribution to the transition from the acute-to-chronic phases of infection.
Copyright © 2010 Institut Pasteur. Published by Elsevier SAS. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Giorgi JV, Hultin LE, McKeating JA, Johnson TD, Owens B, Jacobson LP, Shih R, Lewis J, Wiley DJ, Phair JP, Wolinsky SM, Detels R. Shorter survival in advanced human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection is more closely associated with T lymphocyte activation than with plasma virus burden or virus chemokine coreceptor usage. J Infect Dis. 1999;179:859–870. - PubMed
-
- Orendi JM, Bloem AC, Borleffs JC, Wijnholds FJ, de Vos NM, Nottet HS, Visser MR, Snippe H, Verhoef J, Boucher CA. Activation and cell cycle antigens in CD4+ and CD8+ T cells correlate with plasma human immunodeficiency virus (HIV-1) RNA level in HIV-1 infection. J Infect Dis. 1998;178:1279–1287. - PubMed
-
- Sodora DL, Silvestri G. Immune activation and AIDS pathogenesis. AIDS. 2008;22:439–446. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

