New trends in instrumental design for surface plasmon resonance-based biosensors
- PMID: 20951566
- PMCID: PMC3014383
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bios.2010.09.030
New trends in instrumental design for surface plasmon resonance-based biosensors
Abstract
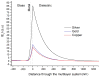
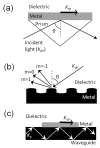
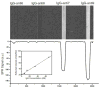
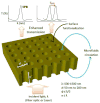
Surface plasmon resonance (SPR)-based biosensing is one of the most advanced label free, real time detection technologies. Numerous research groups with divergent scientific backgrounds have investigated the application of SPR biosensors and studied the fundamental aspects of surface plasmon polaritons that led to new, related instrumentation. As a result, this field continues to be at the forefront of evolving sensing technology. This review emphasizes the new developments in the field of SPR-related instrumentation including optical platforms, chips design, nanoscale approach and new materials. The current tendencies in SPR-based biosensing are identified and the future direction of SPR biosensor technology is broadly discussed.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Abbas A, Dargent T, Croix D, Salzet M, Bocquet B. Medical Science Monitor. 2009a;15:Mt121–Mt125. - PubMed
-
- Abbas A, Treizebre A, Supiot P, Bourzgui NE, Guillochon D, Vercaigne-Marko D, Bocquet B. Biosensors & Bioelectronics. 2009b;25:154–160. - PubMed
-
- Abdulhalim I, Zourob M, Lakhtakia A. Electromagnetics. 2008;28:214–242.
-
- Anker JN, Hall WP, Lyandres O, Shah NC, Zhao J, Van Duyne RP. Nat Mater. 2008;7:442–453. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

