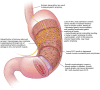
Epidemiology, mechanisms, and management of diabetic gastroparesis
- PMID: 20951838
- PMCID: PMC3035159
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2010.09.022
Epidemiology, mechanisms, and management of diabetic gastroparesis
Abstract
Recent evidence of the significant impact of gastroparesis on morbidity and mortality mandates optimized management of this condition. Gastroparesis affects nutritional state, and in diabetics it has deleterious effects on glycemic control and secondary effects on organs that increase mortality. First-line treatments include restoration of nutrition and medications (prokinetic and antiemetic). We review the epidemiology, pathophysiology, impact, natural history, time trends, and treatment of gastroparesis, focusing on diabetic gastroparesis. We discuss pros and cons of current treatment options, including metoclopramide. Second-line therapeutic approaches include surgery, venting gastrostomy or jejunostomy, and gastric electrical stimulation; most of these were developed based on results from open-label trials. New therapeutic strategies for gastroparesis include drugs that target the underlying defects, prokinetic agents such as 5-hydroxytryptamine agonists that do not appear to have cardiac or vascular effects, ghrelin agonists, approaches to pace the stomach, and stem cell therapies.
Copyright © 2011 AGA Institute. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous