The learning curve for laparoscopic radical prostatectomy: an international multicenter study
- PMID: 20952022
- PMCID: PMC3397250
- DOI: 10.1016/j.juro.2010.08.003
The learning curve for laparoscopic radical prostatectomy: an international multicenter study
Abstract
Purpose: It is not yet possible to estimate the number of cases required for a beginner to become expert in laparoscopic radical prostatectomy. We estimated the learning curve of laparoscopic radical prostatectomy for positive surgical margins compared to a published learning curve for open radical prostatectomy.
Materials and methods: We reviewed records from 8,544 consecutive patients with prostate cancer treated laparoscopically by 51 surgeons at 14 academic institutions in Europe and the United States. The probability of a positive surgical margin was calculated as a function of surgeon experience with adjustment for pathological stage, Gleason score and prostate specific antigen. A second model incorporated prior experience with open radical prostatectomy and surgeon generation.
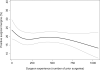
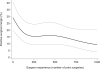
Results: Positive surgical margins occurred in 1,862 patients (22%). There was an apparent improvement in surgical margin rates up to a plateau at 200 to 250 surgeries. Changes in margin rates once this plateau was reached were relatively minimal relative to the CIs. The absolute risk difference for 10 vs 250 prior surgeries was 4.8% (95% CI 1.5, 8.5). Neither surgeon generation nor prior open radical prostatectomy experience was statistically significant when added to the model. The rate of decrease in positive surgical margins was more rapid in the open vs laparoscopic learning curve.
Conclusions: The learning curve for surgical margins after laparoscopic radical prostatectomy plateaus at approximately 200 to 250 cases. Prior open experience and surgeon generation do not improve the margin rate, suggesting that the rate is primarily a function of specifically laparoscopic training and experience.
Copyright © 2010 American Urological Association Education and Research, Inc. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Impact of Experience on the Risk of Surgical Margins and Biochemical Recurrence after Robot-Assisted Radical Prostatectomy: A Learning Curve Study.J Urol. 2019 Jul;202(1):108-113. doi: 10.1097/JU.0000000000000147. Epub 2019 Jun 7. J Urol. 2019. PMID: 30747873 Free PMC article.
-
A comparison of the incidence and location of positive surgical margins in robotic assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy and open retropubic radical prostatectomy.J Urol. 2007 Dec;178(6):2385-9; discussion 2389-90. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2007.08.008. Epub 2007 Oct 22. J Urol. 2007. PMID: 17936849
-
The surgical learning curve for laparoscopic radical prostatectomy: a retrospective cohort study.Lancet Oncol. 2009 May;10(5):475-80. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(09)70079-8. Epub 2009 Apr 1. Lancet Oncol. 2009. PMID: 19342300 Free PMC article.
-
Margin control in robotic and laparoscopic prostatectomy: what are the REAL outcomes?Urol Oncol. 2010 Mar-Apr;28(2):210-4. doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2009.08.009. Urol Oncol. 2010. PMID: 20219561 Review.
-
[Methods for training of robot-assisted radical prostatectomy].Khirurgiia (Mosk). 2019;(1):89-94. doi: 10.17116/hirurgia201901189. Khirurgiia (Mosk). 2019. PMID: 30789615 Review. Russian.
Cited by
-
Complications, urinary continence, and oncologic outcomes of laparoscopic radical prostatectomy: single-surgeon experience for the first 100 cases.Prostate Cancer. 2011;2011:606505. doi: 10.1155/2011/606505. Epub 2011 Jul 14. Prostate Cancer. 2011. PMID: 22110991 Free PMC article.
-
Surgical learning curve for open radical prostatectomy: Is there an end to the learning curve?World J Urol. 2015 Nov;33(11):1721-7. doi: 10.1007/s00345-015-1540-5. Epub 2015 Mar 21. World J Urol. 2015. PMID: 25791787
-
Tumor Biological Feature and Its Association with Positive Surgical Margins and Apical Margins after Radical Prostatectomy in Non-Metastasis Prostate Cancer.Curr Oncol. 2021 Apr 13;28(2):1528-1536. doi: 10.3390/curroncol28020144. Curr Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33924669 Free PMC article.
-
Versatility of 3D laproscopy for radical prostatectomy: A single tertiary cancer center experience.Indian J Surg Oncol. 2022 Sep;13(3):525-532. doi: 10.1007/s13193-022-01518-6. Epub 2022 Feb 14. Indian J Surg Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36187528 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical utility of MRI in the decision-making process before radical prostatectomy: Systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2019 Jan 7;14(1):e0210194. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0210194. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 30615661 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vickers AJ, Bianco FJ, Serio AM, et al. The surgical learning curve for prostate cancer control after radical prostatectomy. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2007;99:1171. - PubMed
-
- Atug F, Castle EP, Srivastav SK, et al. Positive surgical margins in robotic-assisted radical prostatectomy: impact of learning curve on oncologic outcomes. Eur Urol. 2006;49:866. - PubMed

